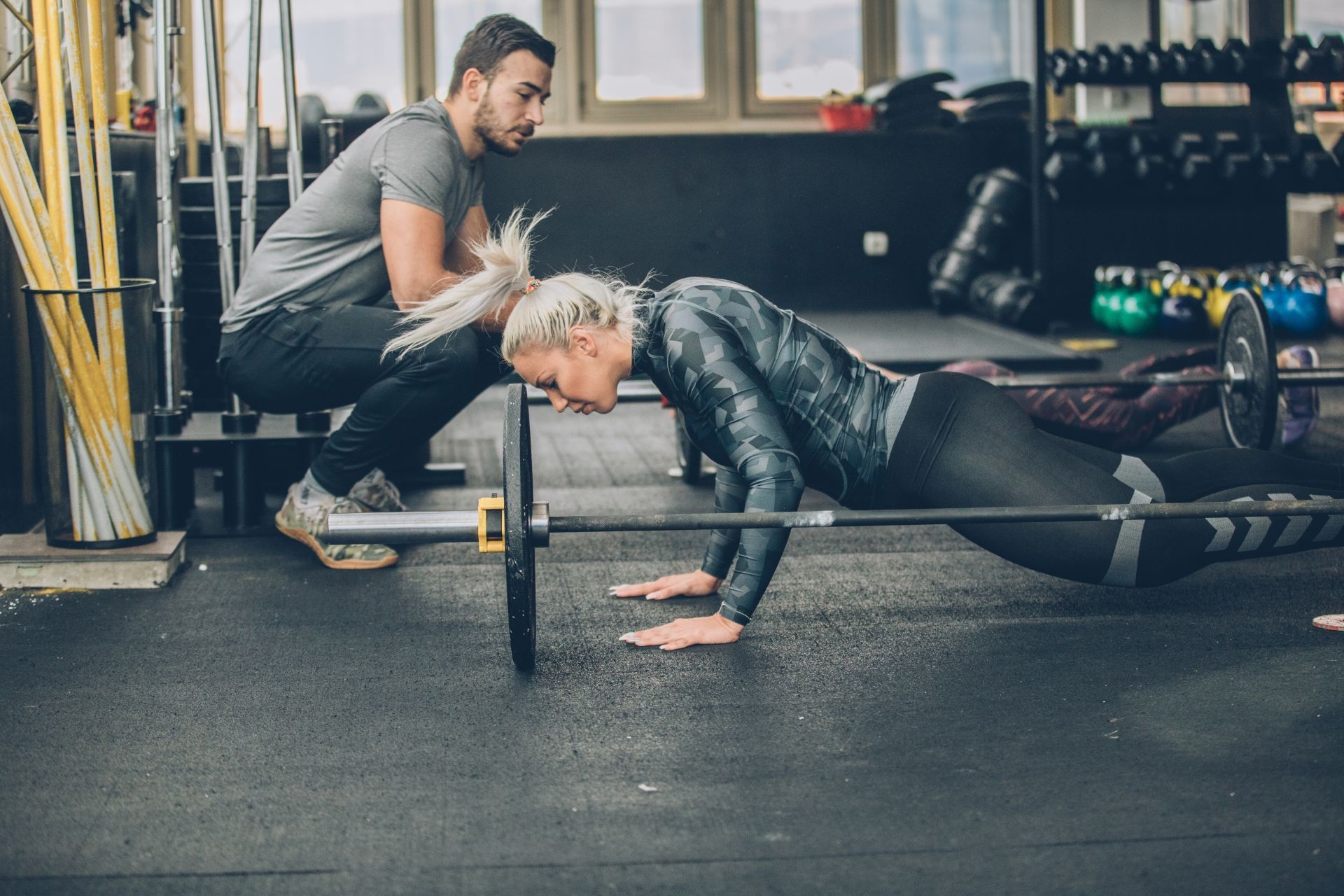


Vestibular rehabilitation is a specialized form of therapy that aims to improve balance and reduce symptoms related to balance disorders. It is designed to target the vestibular system, which is responsible for maintaining balance and spatial orientation. The therapy typically involves a combination of exercises and techniques that focus on improving coordination, strengthening muscles, and enhancing the brain's ability to process sensory information. By addressing the underlying causes of balance disorders, vestibular rehabilitation can help individuals regain their balance, reduce dizziness and vertigo, and improve their overall quality of life.
Common symptoms that can be treated with vestibular rehabilitation include dizziness, vertigo, unsteadiness, and problems with coordination and balance. These symptoms can be caused by various conditions, such as vestibular neuritis, labyrinthitis, Meniere's disease, and benign paroxysmal positional vertigo (BPPV). Vestibular rehabilitation can help alleviate these symptoms by targeting the specific issues within the vestibular system that are causing the imbalance.
A strong core benefits everyone, whether you’re an athlete or office worker. Beyond the abdominal region, your core assists with and supports movement, from how you sit to your form during exercise. Learn more about the core region and the benefits of strengthening these muscles. What Is Your Core? The core region starts with your... The post Benefits of Building a Strong Core appeared first on Integrated Rehabilitation Services.

Posted by on 2023-12-22
The hip is one of the body’s largest and most stable joints. Intended for a wider range of motion, this ball-and-socket-style joint bears a significant amount of weight. It’s also surrounded by various ligaments, tendons and soft tissues for support. An injury to this area can affect your mobility on a broader scale and often... The post Common Types of Hip Injuries appeared first on Integrated Rehabilitation Services.

Posted by on 2023-12-14
As you grow older, your body goes through many changes. These factors not only affect its functionality but can make you more vulnerable to falls and certain chronic conditions. Geriatric physical therapy addresses these needs for patients 65 and older, including injury recovery and prevention. If you are within this age group and your doctor... The post What to Expect During Physical Therapy for Seniors appeared first on Integrated Rehabilitation Services.

Posted by on 2023-12-07
After a serious injury, surgery and recovery can take a toll on the body. Regaining muscle strength can be an uphill battle of slow, incremental progress to reach the level and skill once attained. Blood flow restriction therapy (BFR) partially interrupts this process to aid recovery without greatly impacting muscle strength. Learn more about this... The post Blood Flow Restriction Therapy for Injury Recovery appeared first on Integrated Rehabilitation Services.

Posted by on 2023-10-31
Golf is often perceived as a leisurely activity, yet every time you take a shot, you’re engaging the hips, back, legs and arms. The repetition of gripping and swinging a golf club, coupled with potentially poor form, can place significant strain on these areas of the body. Learn about common golf injuries and prevention tactics... The post Common Golf Injuries appeared first on Integrated Rehabilitation Services.

Posted by on 2023-10-20
The duration of a typical vestibular rehabilitation program can vary depending on the individual's condition and progress. Generally, a program may last for several weeks to a few months. The frequency of sessions is typically determined by the therapist and may range from one to three sessions per week. The therapist will assess the individual's progress and adjust the program accordingly to ensure optimal results.
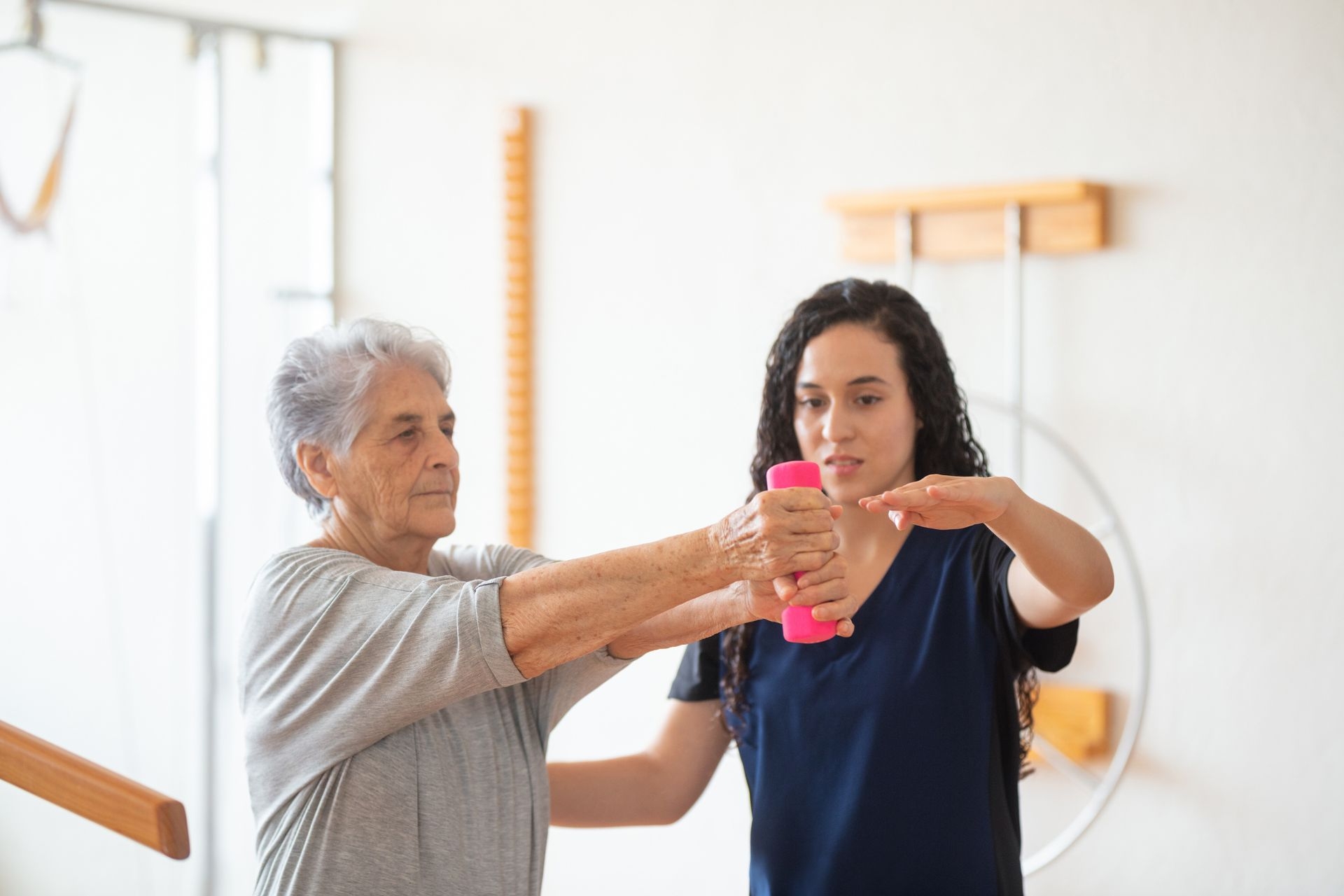

Vestibular rehabilitation involves a range of exercises and techniques tailored to the individual's specific needs. These may include gaze stabilization exercises, balance training, habituation exercises, and canalith repositioning maneuvers for BPPV. Gaze stabilization exercises aim to improve the ability to focus on a target while the head is in motion, while balance training focuses on improving stability and coordination. Habituation exercises involve gradually exposing the individual to movements or positions that trigger their symptoms, helping them become desensitized over time. Canalith repositioning maneuvers are specific techniques used to reposition displaced calcium crystals in the inner ear, which can cause BPPV.
Yes, vestibular rehabilitation can be effective in treating vertigo and dizziness caused by inner ear problems. Inner ear disorders, such as BPPV, vestibular neuritis, and Meniere's disease, can disrupt the normal functioning of the vestibular system, leading to symptoms like vertigo and dizziness. Vestibular rehabilitation targets these underlying issues by improving the function of the vestibular system and helping the brain adapt to the changes. Through a combination of exercises and techniques, individuals can experience a reduction in vertigo and dizziness, leading to improved balance and overall well-being.
Standard PT Rehab Techniques To Ask Your Physical Therapist About
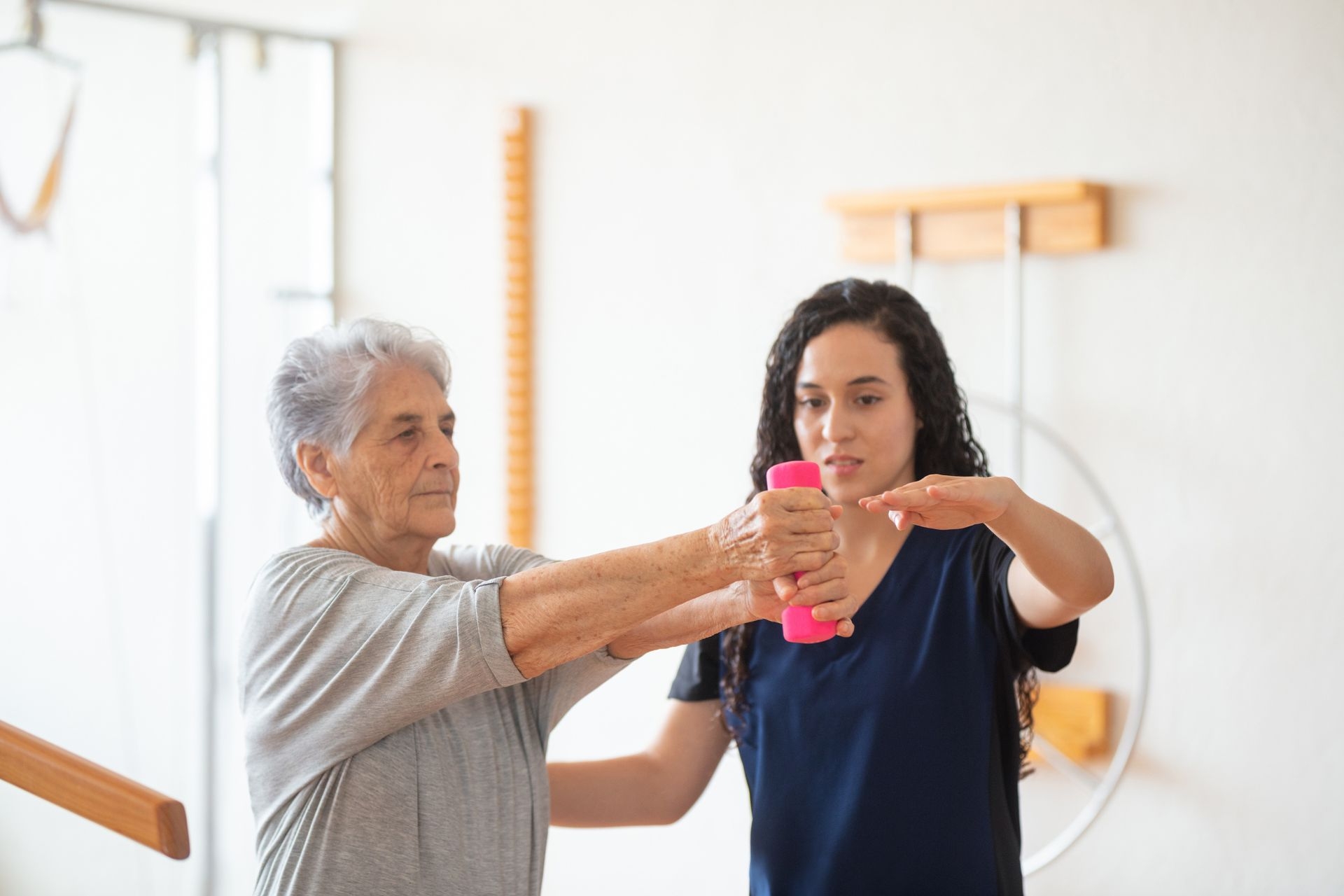

The potential risks or side effects of vestibular rehabilitation are generally minimal. However, some individuals may experience temporary dizziness or increased symptoms during the initial stages of therapy as their vestibular system is being challenged and retrained. These symptoms typically subside as the therapy progresses and the individual's balance improves. It is important to work with a qualified therapist who can monitor and adjust the program to ensure safety and minimize any potential risks.
The coverage of vestibular rehabilitation by insurance can vary depending on the specific insurance plan. In many cases, vestibular rehabilitation is covered by insurance, especially when it is deemed medically necessary. However, it is important to check with the insurance provider to determine the extent of coverage and any potential out-of-pocket costs. The cost of vestibular rehabilitation can also vary depending on factors such as location and the duration of the program. It is recommended to consult with a healthcare provider or therapist to get a better understanding of the costs involved and any potential financial assistance options that may be available.
Potential risks associated with instrument-assisted soft tissue mobilization (IASTM) techniques include bruising, skin irritation, and potential exacerbation of underlying conditions such as inflammation or infection. Improper use of the tools or excessive pressure during the technique can lead to tissue damage or nerve injury. Additionally, if the practitioner is not properly trained in IASTM, there is a risk of causing harm to the patient. It is important for practitioners to thoroughly assess the patient's medical history and current condition before performing IASTM to minimize the risk of complications. Furthermore, patients with certain medical conditions such as blood clotting disorders or compromised skin integrity may not be suitable candidates for IASTM due to the increased risk of adverse effects.
Foam rolling is a widely used technique in physical therapy rehabilitation for myofascial release. The benefits of using a foam roller for myofascial release in PT rehabilitation are numerous. Firstly, foam rolling helps to break up adhesions and knots in the fascia, which is the connective tissue that surrounds and supports the muscles. This can help to improve flexibility and range of motion, as well as reduce pain and discomfort. Additionally, foam rolling can increase blood flow to the muscles, which can aid in the healing process and promote tissue repair. It can also help to improve muscle performance and prevent injuries by reducing muscle imbalances and tightness. Furthermore, foam rolling can be used as a self-massage tool, allowing individuals to target specific areas of tightness or discomfort. Overall, incorporating foam rolling into PT rehabilitation can be highly beneficial for improving mobility, reducing pain, and enhancing overall muscle function.
When prescribing Nordic hamstring exercises for injury prevention, there are several considerations that need to be taken into account. Firstly, the athlete's current level of fitness and strength should be assessed to ensure that they are capable of performing the exercise safely and effectively. Secondly, the frequency and intensity of the exercise should be tailored to the individual's needs and goals. Thirdly, the exercise should be incorporated into a comprehensive training program that includes other exercises and activities that target the same muscle groups and movement patterns. Fourthly, proper technique and form should be emphasized to minimize the risk of injury and maximize the benefits of the exercise. Finally, the athlete's progress should be monitored and adjustments made as necessary to ensure that they continue to make gains and avoid injury.
Endurance athletes can prevent overuse injuries by implementing a variety of strategies. These include gradually increasing training intensity and duration, incorporating proper rest and recovery periods, cross-training to reduce repetitive stress on specific muscles and joints, maintaining proper nutrition and hydration, using proper equipment and footwear, and regularly performing strength and flexibility exercises to improve overall muscle balance and joint stability. Additionally, athletes can benefit from working with a coach or trainer to develop a well-rounded training plan that takes into account individual biomechanics and potential areas of weakness or imbalance. By following these strategies, endurance athletes can reduce the risk of overuse injuries and maintain long-term performance and health.
The Graston Technique facilitates tissue healing and remodeling in PT rehabilitation by utilizing specially designed stainless steel instruments to effectively detect and treat areas of soft tissue fibrosis or chronic inflammation. This technique helps to break down scar tissue and fascial restrictions, promoting the resorption of fibrotic tissue and stimulating the production of new collagen. By targeting adhesions and scar tissue, the Graston Technique promotes improved blood flow, tissue repair, and the remodeling of affected tissues. This process ultimately leads to improved range of motion, reduced pain, and enhanced functional recovery for patients undergoing physical therapy rehabilitation.
Several studies have provided evidence supporting the use of Pilates-based rehabilitation for improving core stability. A systematic review conducted by Smith et al. (2015) found that Pilates exercises significantly improved core stability in healthy individuals and those with low back pain. Another study by Wells et al. (2012) demonstrated that Pilates-based rehabilitation was effective in improving core stability and reducing pain in individuals with chronic low back pain. Additionally, a randomized controlled trial by Rydeard et al. (2006) showed that Pilates exercises improved core stability and reduced disability in patients with non-specific low back pain. These findings suggest that Pilates-based rehabilitation can be an effective intervention for enhancing core stability in various populations.
When prescribing therapeutic ultrasound for tendonitis rehabilitation, there are several key considerations that need to be taken into account. Firstly, the therapist should assess the severity and stage of the tendonitis to determine the appropriate treatment protocol. This may involve considering factors such as the location of the tendonitis, the extent of inflammation, and the presence of any underlying conditions. Additionally, the therapist should consider the patient's individual characteristics, such as their age, overall health, and tolerance to ultrasound therapy. It is also important to consider the specific goals of the rehabilitation program and how ultrasound can be integrated into a comprehensive treatment plan. Furthermore, the therapist should be knowledgeable about the different ultrasound parameters, such as frequency, intensity, and treatment duration, and how they can be adjusted to optimize the therapeutic effects. Finally, regular monitoring and reassessment of the patient's progress should be conducted to ensure that the ultrasound therapy is effective and appropriate adjustments can be made if necessary.