
NLP, or natural language processing, can be used in rehabilitation for stroke patients in several ways. One application is in speech therapy, where NLP techniques can help analyze and improve the patient's speech and language abilities. For example, NLP algorithms can be used to assess the patient's speech patterns and identify areas of improvement, such as pronunciation or grammar. Additionally, NLP can be used to develop interactive virtual reality environments that simulate real-life scenarios, allowing stroke patients to practice their communication skills in a safe and controlled setting. These virtual environments can provide personalized feedback and guidance, helping patients regain their language abilities more effectively.
When it comes to individuals with spinal cord injuries, NLP techniques can be applied to assist with various aspects of their rehabilitation. One specific technique is the use of predictive text algorithms to aid in communication. For individuals with limited mobility or paralysis, typing or speaking can be challenging. NLP algorithms can predict the intended words or phrases based on partial input, making communication faster and more efficient. Additionally, NLP can be used to develop assistive technologies that enable individuals with spinal cord injuries to control external devices, such as wheelchairs or robotic limbs, using their thoughts or voice commands. These advancements in NLP can greatly enhance the independence and quality of life for individuals with spinal cord injuries.
Standard PT Rehab Techniques To Ask Your Physical Therapist About
For athletes and avid gym-goers, it’s common to feel pain around the hip or outside of the knee. One cause is a swollen or inflamed iliotibial (IT) band, the thick tendon that passes from the pelvis to the shin bone along the outside of the leg and helps with extension. Repetitive motion can cause the... The post What Is IT Band Syndrome? appeared first on Integrated Rehabilitation Services.

Posted by on 2024-02-22
Your ribs play a protective role, shielding your lungs and chest cavity from impact. Yet these forces may be sharp enough to break a rib or two, resulting in pain and breathing difficulties. Recovery following a broken rib often involves strengthening the area and addressing breathing concerns. Learn what to expect from physical therapy. How... The post Physical Therapy for a Broken Rib appeared first on Integrated Rehabilitation Services.

Posted by on 2024-01-29
All forms of dance combine artistry with strength, focus and athleticism. Among professionals and dedicated students, flexibility and agility are required, as well as hours of intensive training. Dance might involve the whole body but heavily relies on the feet, legs and ankles. As such, years of intensive training and performance schedules place extensive wear... The post Common Dance Injuries appeared first on Integrated Rehabilitation Services.

Posted by on 2024-01-16
While you can experience a fall injury at any age, risks and severity increase as you grow older. Especially for adults 65 and over, falls may negatively impact quality of life, resulting in reduced mobility, less socialization, cognitive health decline and higher risks for a subsequent fall injury. Physical therapy serves three key roles: injury... The post Physical Therapy After a Fall Injury appeared first on Integrated Rehabilitation Services.

Posted by on 2024-01-03
A strong core benefits everyone, whether you’re an athlete or office worker. Beyond the abdominal region, your core assists with and supports movement, from how you sit to your form during exercise. Learn more about the core region and the benefits of strengthening these muscles. What Is Your Core? The core region starts with your... The post Benefits of Building a Strong Core appeared first on Integrated Rehabilitation Services.

Posted by on 2023-12-22
There is a growing body of research supporting the effectiveness of NLP in rehabilitation for traumatic brain injury (TBI). Studies have shown that NLP techniques can be used to improve cognitive functions, such as attention, memory, and problem-solving skills, in individuals with TBI. For example, NLP algorithms can be used to develop computer-based cognitive training programs that adapt to the individual's specific needs and progress. These programs can provide personalized exercises and feedback, helping individuals with TBI regain cognitive abilities more effectively. Additionally, NLP can be used to analyze and interpret data from brain imaging techniques, such as functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI), to better understand the neural mechanisms underlying TBI and guide targeted rehabilitation interventions.
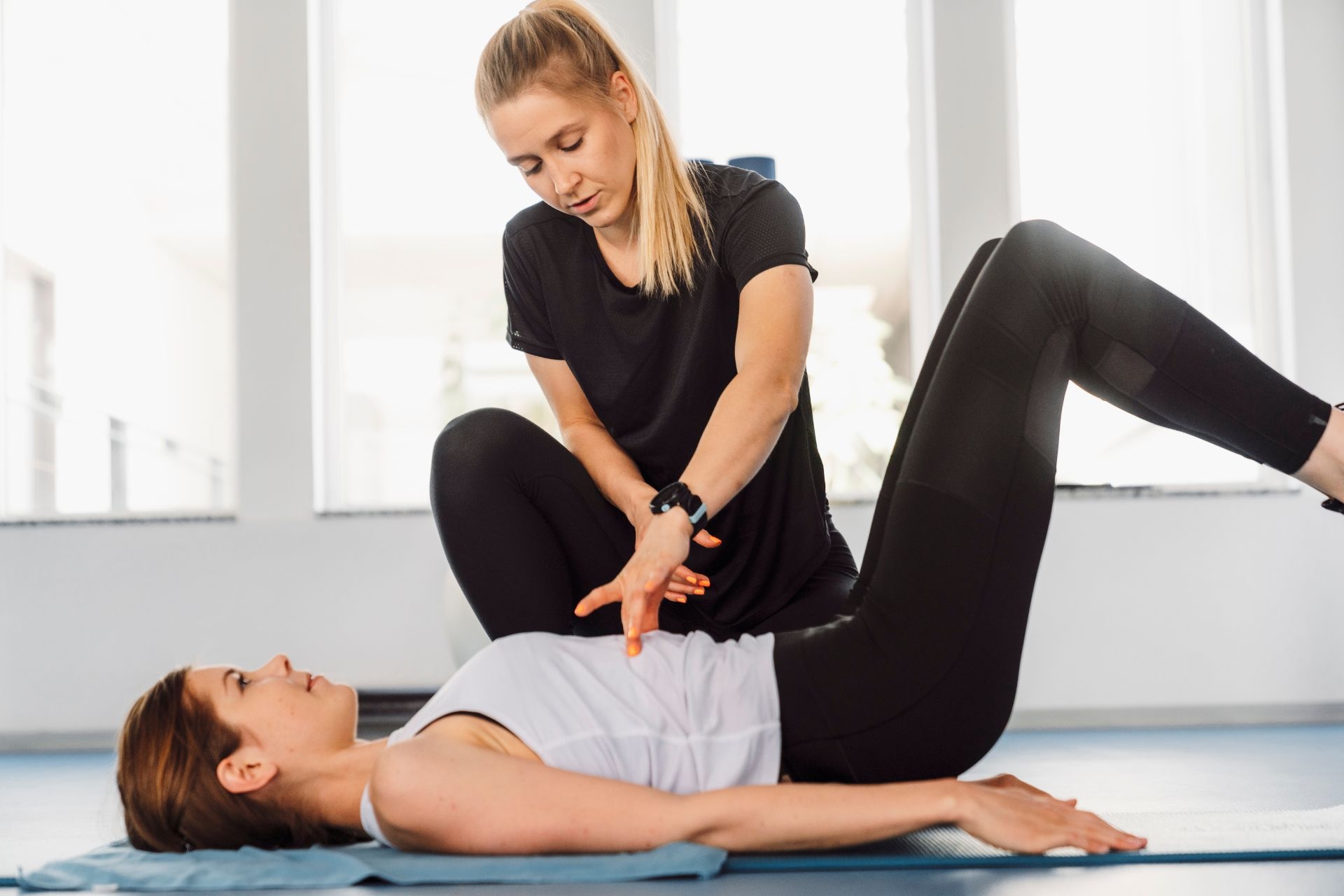

NLP can be integrated into physical therapy for individuals recovering from orthopedic injuries in various ways. One application is in the development of virtual reality-based rehabilitation programs. NLP algorithms can be used to analyze the patient's movements and provide real-time feedback on their posture, alignment, and range of motion. This feedback can help individuals correct their movements and perform exercises more accurately, leading to better outcomes in their recovery. Additionally, NLP can be used to develop personalized exercise programs that adapt to the individual's progress and goals. These programs can provide step-by-step instructions and guidance, ensuring that individuals perform exercises correctly and safely.
NLP plays a significant role in helping individuals with chronic pain management during rehabilitation. One application is in the development of chatbot-based interventions. NLP algorithms can be used to analyze the patient's pain descriptions and provide personalized recommendations for pain management techniques, such as relaxation exercises, mindfulness meditation, or medication adjustments. These chatbots can also provide emotional support and encouragement, helping individuals cope with the psychological aspects of chronic pain. Additionally, NLP can be used to analyze large amounts of patient data, such as pain diaries or medical records, to identify patterns and trends that can inform personalized pain management strategies.
Yes, NLP can be used to address psychological barriers to rehabilitation for individuals with amputations. One approach is the use of cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) techniques delivered through virtual reality environments. NLP algorithms can be used to analyze the patient's thoughts, emotions, and behaviors, and provide personalized CBT interventions within the virtual environment. For example, the virtual therapist can guide the individual through exposure therapy exercises, helping them confront and overcome their fears or anxieties related to their amputation. Additionally, NLP can be used to develop interactive self-help tools, such as mobile applications or online platforms, that provide individuals with amputations with resources and support for managing their psychological well-being during the rehabilitation process.
Standard PT Rehab Techniques To Ask Your Physical Therapist About
There are specialized NLP programs and interventions designed for children undergoing rehabilitation for developmental disabilities. These programs often focus on improving language and communication skills, social interactions, and cognitive abilities. For example, NLP algorithms can be used to develop interactive storytelling applications that adapt to the child's language level and provide personalized feedback and guidance. These applications can help children with developmental disabilities improve their vocabulary, comprehension, and narrative skills. Additionally, NLP can be used to develop social skills training programs that simulate real-life social situations and provide personalized feedback on the child's social interactions. These specialized NLP interventions can greatly enhance the rehabilitation process for children with developmental disabilities, promoting their overall development and well-being.
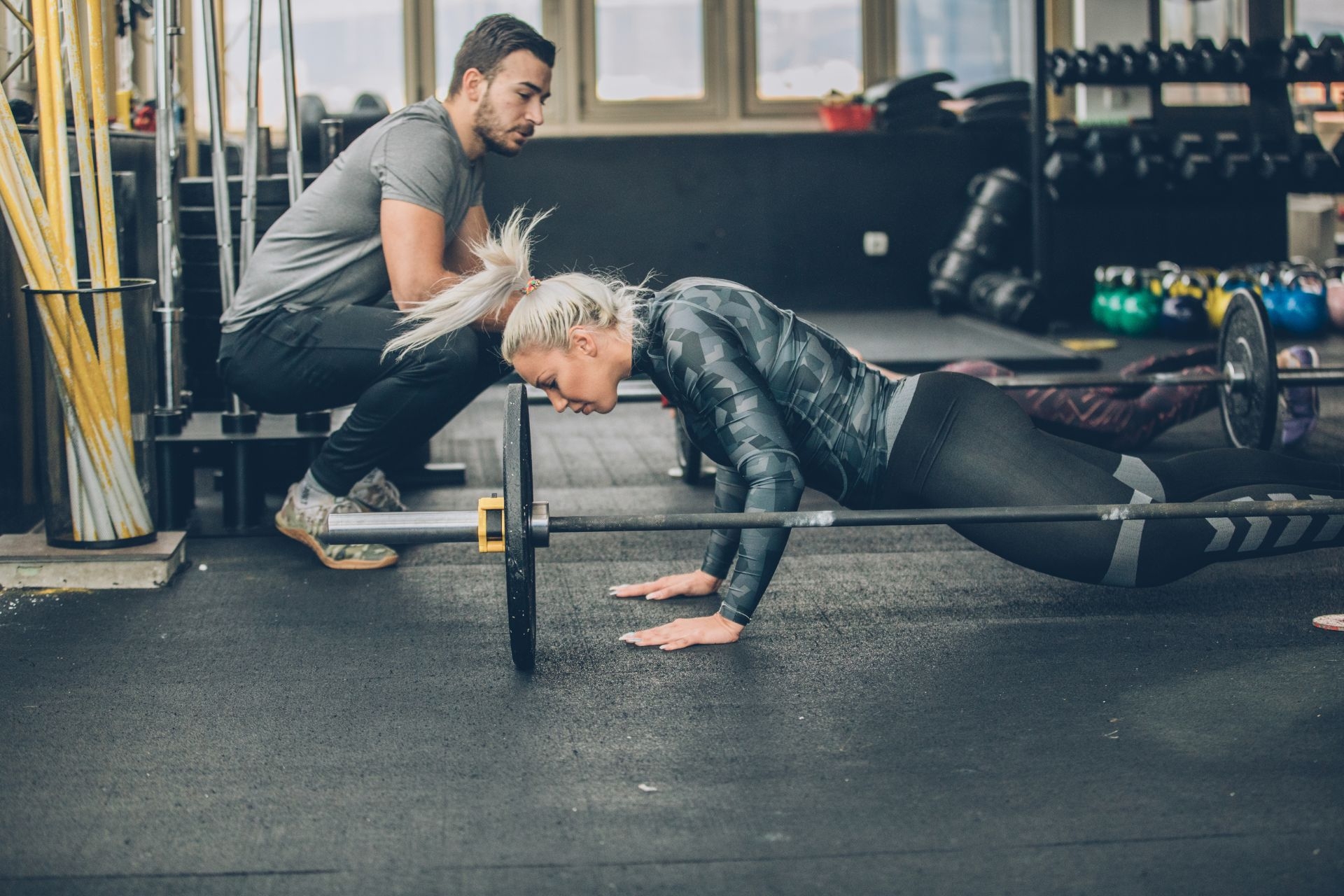

Therapists employ various assessment techniques to evaluate and treat muscle imbalances in shoulder rehabilitation programs. They may conduct a thorough physical examination to assess the range of motion, strength, and stability of the shoulder joint. This evaluation may involve specific tests such as the Hawkins-Kennedy test, Neer test, or Jobe test to identify any impingement or rotator cuff issues. Additionally, therapists may use electromyography (EMG) to measure muscle activity and identify any imbalances or weaknesses. Once the imbalances are identified, therapists can address them through a combination of targeted exercises, stretching, and manual therapy techniques. These interventions may include strengthening exercises for weak muscles, stretching exercises for tight muscles, and techniques such as myofascial release or joint mobilization to restore proper alignment and function. By addressing muscle imbalances, therapists aim to restore optimal shoulder function and prevent future injuries.
The Mulligan concept and Maitland approach are two different manual therapy techniques used in physical therapy rehabilitation. The key differences between these approaches lie in their underlying principles and treatment techniques. The Mulligan concept, developed by Brian Mulligan, focuses on the concept of mobilization with movement (MWM) and emphasizes the use of pain-free techniques to restore joint function and reduce pain. It involves the application of sustained glides or accessory movements to the joint while the patient performs specific active movements. On the other hand, the Maitland approach, developed by Geoffrey Maitland, is based on the principles of passive joint mobilization and graded oscillatory movements. It involves the therapist applying graded pressure and oscillatory movements to the joint to restore its range of motion and reduce pain. While both approaches aim to improve joint function and reduce pain, the Mulligan concept places more emphasis on active patient participation and pain-free techniques, whereas the Maitland approach focuses on passive joint mobilization and graded oscillatory movements.
Cupping therapy has been shown to influence tissue perfusion and pain modulation in physical therapy (PT) rehabilitation. The application of negative pressure through the use of cups can lead to increased blood flow, improved microcirculation, and enhanced tissue oxygenation, ultimately promoting tissue perfusion. This can result in accelerated healing, reduced inflammation, and improved tissue repair, which are all crucial components of the rehabilitation process. Additionally, cupping therapy has been found to stimulate the release of endorphins and other neuropeptides, leading to pain modulation and relief. By targeting trigger points and areas of pain, cupping therapy can help alleviate discomfort and improve overall function, making it a valuable adjunct to PT rehabilitation programs.
There are several psychological factors that can influence adherence to home exercise programs. One important factor is motivation, which can be influenced by a person's beliefs, values, and goals. For example, if someone believes that exercise is important for their overall health and has a goal of improving their fitness level, they may be more motivated to stick to their home exercise program. Another factor is self-efficacy, which refers to a person's belief in their ability to successfully complete a task. If someone has high self-efficacy for exercise, they are more likely to believe that they can successfully complete their home exercise program and are therefore more likely to adhere to it. Additionally, social support can play a role in adherence. Having support from friends, family, or a workout buddy can provide encouragement and accountability, making it more likely that a person will stick to their home exercise program. Finally, enjoyment of the exercise itself can also influence adherence. If someone finds their home exercise program enjoyable and engaging, they are more likely to continue with it over time.
Individuals with hypermobility syndromes require exercise programs that are tailored to their specific needs. Therapists modify exercise programs by focusing on stability and strengthening exercises that target the muscles surrounding the hypermobile joints. These exercises aim to improve joint stability and reduce the risk of injury. Therapists also incorporate low-impact exercises, such as swimming or cycling, to reduce the stress on the joints. Additionally, therapists may use props, such as resistance bands or stability balls, to provide additional support during exercises. It is important for therapists to monitor the individual's progress and adjust the exercise program accordingly to ensure that it is effective and safe.