

Functional Electrical Stimulation (FES) is a therapeutic technique that uses electrical currents to stimulate specific muscles or muscle groups. It works by delivering small, controlled electrical pulses to the nerves that control the targeted muscles, causing them to contract and produce a functional movement. This can be particularly beneficial for individuals with neurological conditions or injuries that have resulted in muscle weakness or paralysis.
FES can benefit individuals with a variety of medical conditions or injuries, including stroke, spinal cord injury, multiple sclerosis, cerebral palsy, and traumatic brain injury. It can also be used for individuals with muscle atrophy or weakness due to disuse or prolonged bed rest. Additionally, FES has been shown to be effective in improving muscle strength and function in individuals with conditions such as foot drop, where the muscles that lift the foot are weak or paralyzed.
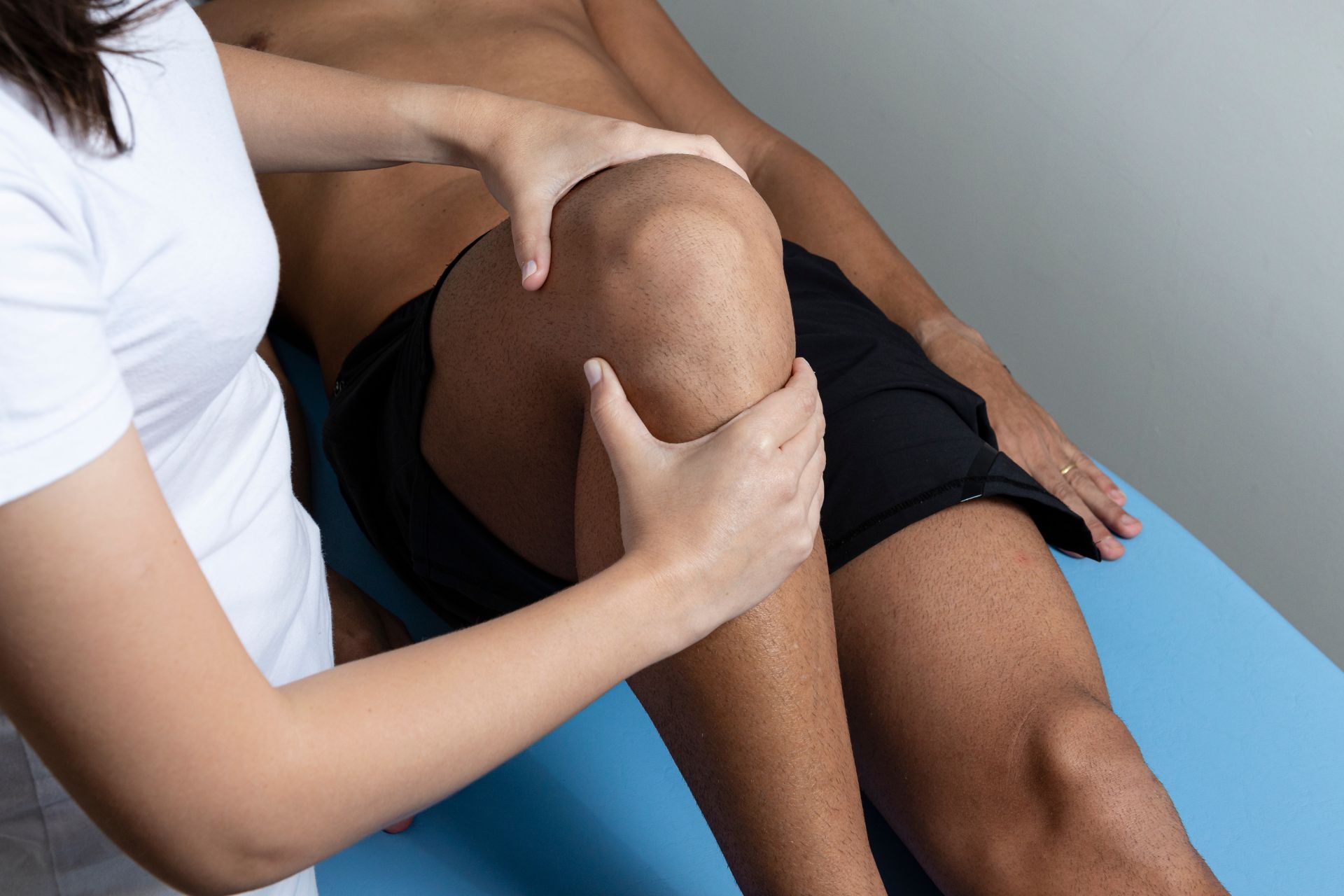
Standard PT Rehab Techniques To Ask Your Physical Therapist About
The hip is one of the body’s largest and most stable joints. Intended for a wider range of motion, this ball-and-socket-style joint bears a significant amount of weight. It’s also surrounded by various ligaments, tendons and soft tissues for support. An injury to this area can affect your mobility on a broader scale and often... The post Common Types of Hip Injuries appeared first on Integrated Rehabilitation Services.

Posted by on 2023-12-14
As you grow older, your body goes through many changes. These factors not only affect its functionality but can make you more vulnerable to falls and certain chronic conditions. Geriatric physical therapy addresses these needs for patients 65 and older, including injury recovery and prevention. If you are within this age group and your doctor... The post What to Expect During Physical Therapy for Seniors appeared first on Integrated Rehabilitation Services.

Posted by on 2023-12-07
After a serious injury, surgery and recovery can take a toll on the body. Regaining muscle strength can be an uphill battle of slow, incremental progress to reach the level and skill once attained. Blood flow restriction therapy (BFR) partially interrupts this process to aid recovery without greatly impacting muscle strength. Learn more about this... The post Blood Flow Restriction Therapy for Injury Recovery appeared first on Integrated Rehabilitation Services.

Posted by on 2023-10-31
Golf is often perceived as a leisurely activity, yet every time you take a shot, you’re engaging the hips, back, legs and arms. The repetition of gripping and swinging a golf club, coupled with potentially poor form, can place significant strain on these areas of the body. Learn about common golf injuries and prevention tactics... The post Common Golf Injuries appeared first on Integrated Rehabilitation Services.

Posted by on 2023-10-20
Throughout your body, tendons keep the muscles secure to the bones. Although tendons are built to handle significant force, factors like repeat wear and tear, certain diseases, steroid use or an untreated injury can cause this thick, fibrous tissue to tear or snap, resulting in a rupture. The risk of partial and full tendon tears... The post How Does a Ruptured Tendon Occur? appeared first on Integrated Rehabilitation Services.

Posted by on 2023-09-01
FES differs from other forms of electrical stimulation therapy in that it is specifically designed to produce functional movements by targeting the nerves that control the muscles. Unlike other forms of electrical stimulation, which may focus on pain relief or muscle relaxation, FES is aimed at improving muscle strength, coordination, and function.
Potential risks or side effects associated with FES may include skin irritation or discomfort at the site of electrode placement. In some cases, individuals may experience muscle soreness or fatigue following FES sessions. It is important for individuals undergoing FES to be monitored by a healthcare professional to ensure that the treatment is being administered safely and effectively.
FES can be used as a standalone treatment for muscle rehabilitation, particularly for individuals with neurological conditions or injuries that have resulted in muscle weakness or paralysis. However, it is often used in combination with other therapies, such as physical therapy or occupational therapy, to maximize the benefits of muscle stimulation and promote overall functional recovery.

There are specific contraindications for using FES, including the presence of an implanted electronic device, such as a pacemaker or defibrillator, as well as open wounds or skin infections at the site of electrode placement. Additionally, individuals with certain medical conditions, such as epilepsy or certain types of cancer, may not be suitable candidates for FES.
The potential long-term effects of using FES for muscle rehabilitation may include improved muscle strength, endurance, and coordination, leading to enhanced functional abilities and independence in activities of daily living. Additionally, FES may help to prevent muscle atrophy and promote muscle re-education, allowing individuals to maintain or regain the ability to perform specific movements and tasks. Ongoing research continues to explore the long-term benefits of FES for muscle rehabilitation in various patient populations.

When utilizing the BAPS board in ankle rehabilitation exercises, there are several best practices to consider. Firstly, it is important to start with a proper warm-up to prepare the ankle for the exercises. This can include gentle stretching and range of motion exercises. Secondly, it is recommended to start with simple exercises that focus on balance and stability, such as standing on one leg on the BAPS board. As the ankle strength and stability improve, more advanced exercises can be introduced, such as performing squats or lunges on the board. It is crucial to maintain proper form and alignment throughout the exercises to avoid any unnecessary strain on the ankle. Additionally, it is advisable to progress gradually and increase the difficulty of the exercises over time. This can be done by adjusting the angle of the board or introducing additional challenges, such as performing the exercises with eyes closed. Regular and consistent practice is key to achieving optimal results in ankle rehabilitation using the BAPS board.
Eccentric loading exercises play a crucial role in the rehabilitation of Achilles tendon injuries. These exercises involve lengthening the muscle-tendon unit while it is under tension, which helps to stimulate the healing process and improve the strength and flexibility of the tendon. By specifically targeting the eccentric phase of muscle contraction, these exercises help to promote collagen synthesis and remodeling, which are essential for tendon repair. Additionally, eccentric loading exercises can enhance the neuromuscular control and proprioception of the lower limb, reducing the risk of re-injury. Some commonly prescribed eccentric loading exercises for Achilles tendon rehabilitation include heel drops, eccentric calf raises, and eccentric squats. These exercises should be performed under the guidance of a qualified healthcare professional to ensure proper technique and progression.
The Alexander Technique is often recommended as a complementary therapy for individuals suffering from chronic neck pain. This technique focuses on improving posture, body alignment, and movement coordination, which are all crucial factors in managing neck pain. By addressing the underlying causes of poor posture and movement habits, the Alexander Technique aims to alleviate tension and strain in the neck muscles, reducing pain and promoting long-term relief. Additionally, this approach emphasizes body awareness and mindfulness, allowing individuals to develop a better understanding of their own movement patterns and make conscious adjustments to prevent further neck pain. Overall, the Alexander Technique can be a valuable tool in the comprehensive treatment of chronic neck pain, providing individuals with practical skills to improve their posture and movement habits, ultimately leading to reduced pain and improved quality of life.
Therapists address scar tissue adhesions in post-surgical rehabilitation by utilizing various techniques such as manual therapy, massage, stretching, and exercise. They may also incorporate modalities like ultrasound, electrical stimulation, and heat therapy to help break down scar tissue and improve tissue mobility. Additionally, therapists may use myofascial release and instrument-assisted soft tissue mobilization to target specific adhesions and promote tissue healing. By addressing scar tissue adhesions, therapists aim to restore range of motion, reduce pain, and improve overall function for their patients during the rehabilitation process.
Hydrotherapy, also known as aquatic therapy, has been shown to potentially alleviate symptoms in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. This form of therapy involves exercises and movements performed in a warm water pool, which can provide relief and improve joint mobility. The buoyancy of the water reduces the impact on the joints, allowing for gentle movements without causing excessive strain. Additionally, the warmth of the water can help to relax muscles and reduce pain. Hydrotherapy may also promote circulation and reduce inflammation, which are common symptoms of rheumatoid arthritis. Overall, hydrotherapy offers a promising approach for managing symptoms and improving the quality of life for individuals with rheumatoid arthritis.