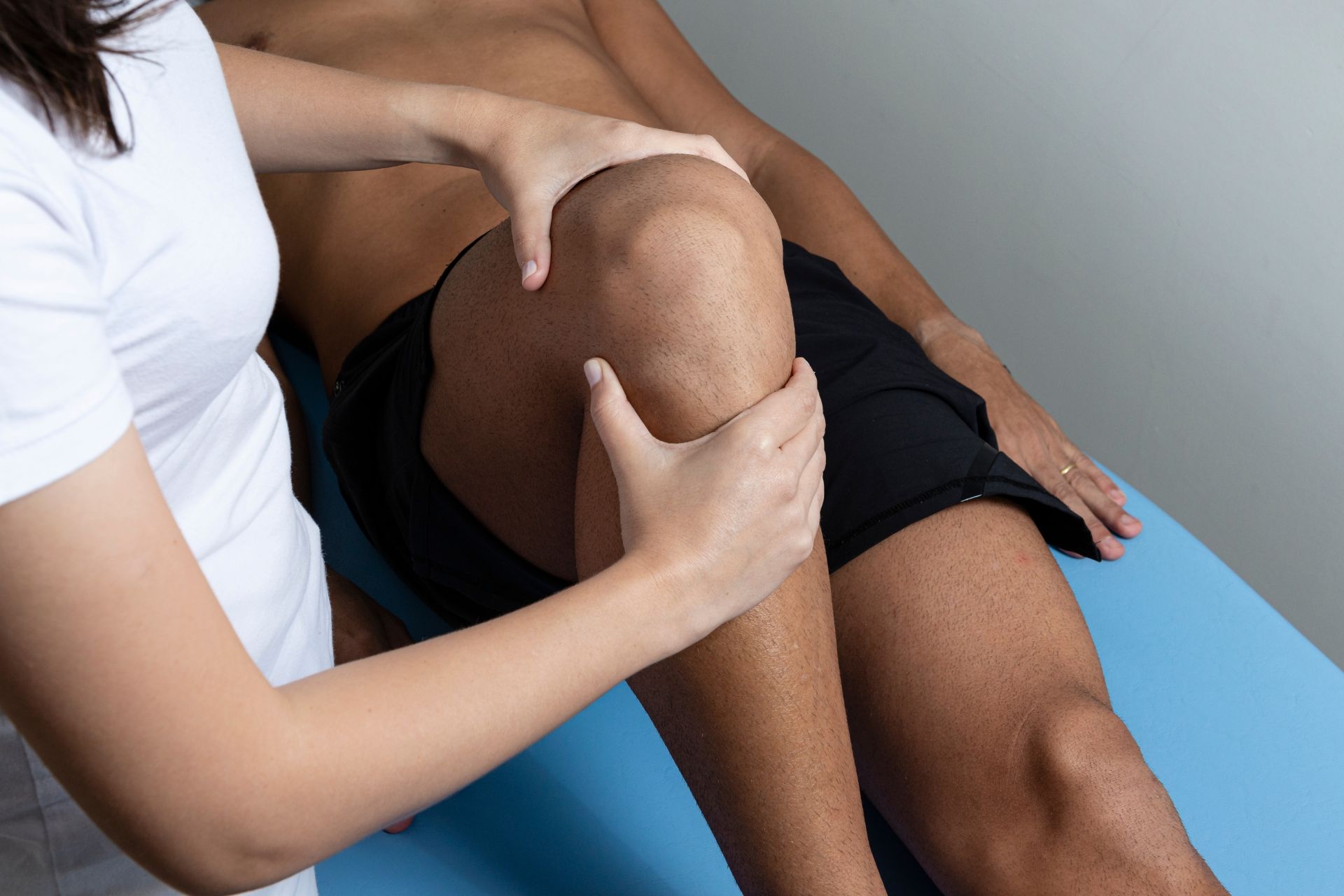

The Rood approach in physical therapy offers several benefits. Firstly, it helps in promoting the development of normal movement patterns and motor control. By utilizing sensory stimulation techniques, the Rood approach can facilitate the activation of specific muscle groups and enhance coordination. Additionally, this approach can improve muscle strength and flexibility, leading to increased functional abilities. The Rood approach also focuses on sensory integration, which can help individuals with sensory processing difficulties to better regulate their responses to sensory stimuli. Overall, the Rood approach is effective in addressing various physical impairments and promoting optimal movement patterns.
The Rood approach is highly effective in improving muscle tone and coordination. This approach utilizes sensory stimulation techniques, such as tapping, brushing, and vibration, to elicit specific responses from the muscles. By providing sensory input to the muscles, the Rood approach can facilitate muscle contraction and relaxation, leading to improved muscle tone. Additionally, the sensory stimulation techniques used in this approach can enhance proprioception, which is the body's ability to sense its position and movement in space. This improved proprioception contributes to better coordination and motor control, allowing individuals to perform movements with greater precision and efficiency.
Standard PT Rehab Techniques To Ask Your Physical Therapist About
Throughout your body, tendons keep the muscles secure to the bones. Although tendons are built to handle significant force, factors like repeat wear and tear, certain diseases, steroid use or an untreated injury can cause this thick, fibrous tissue to tear or snap, resulting in a rupture. The risk of partial and full tendon tears... The post How Does a Ruptured Tendon Occur? appeared first on Integrated Rehabilitation Services.

Posted by on 2023-09-01
The key principles of the Rood approach include the use of sensory stimulation, the application of developmental sequences, and the utilization of facilitation and inhibition techniques. Sensory stimulation involves providing specific sensory input to elicit desired motor responses. Developmental sequences refer to the progression of movement patterns from simple to complex, following the typical developmental milestones. Facilitation techniques are used to enhance muscle activation and movement, while inhibition techniques are employed to reduce unwanted muscle activity. These principles guide the implementation of the Rood approach and help in achieving the desired therapeutic outcomes.
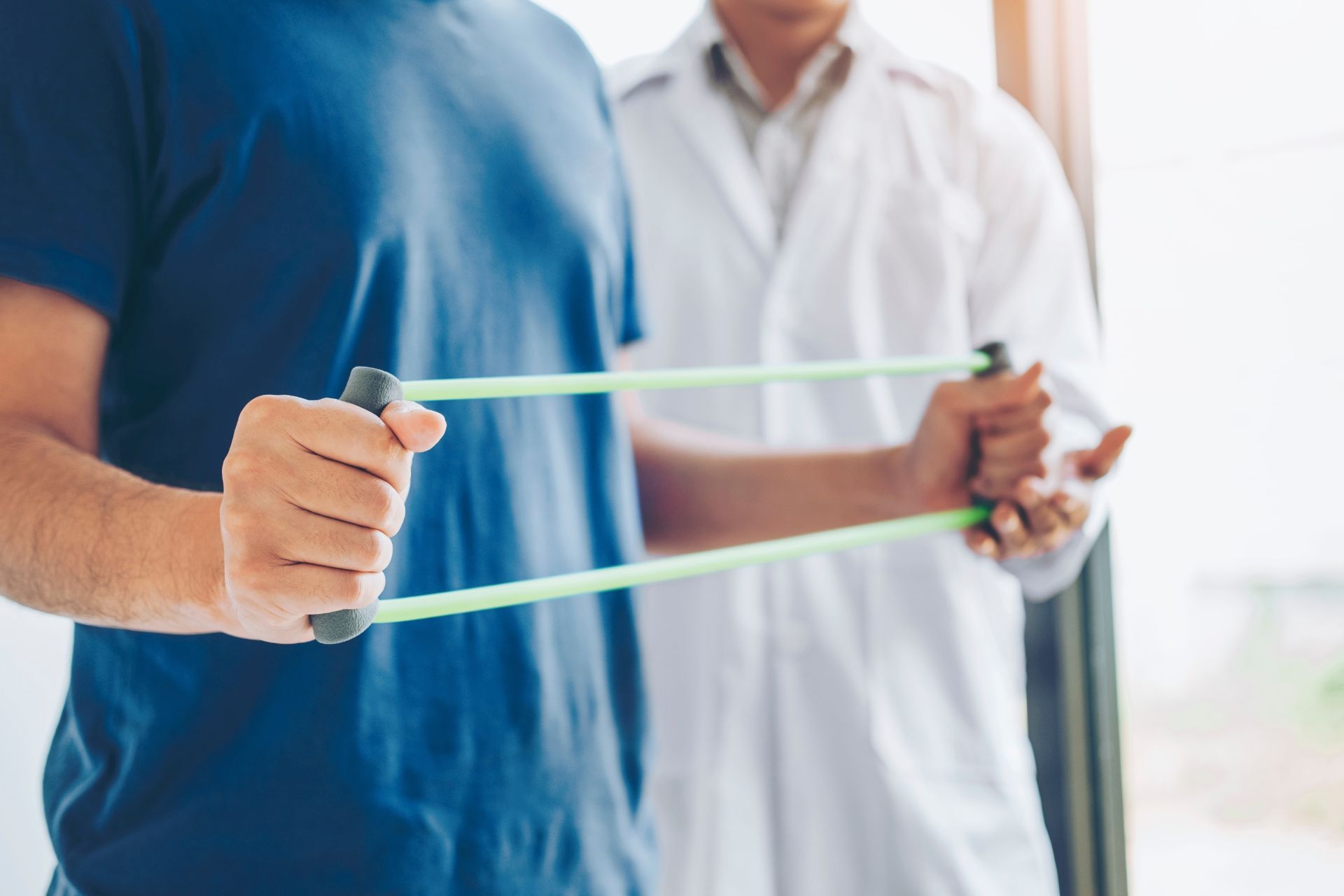

The Rood approach addresses sensory integration and motor control by utilizing sensory stimulation techniques and facilitating appropriate motor responses. Sensory integration refers to the brain's ability to process and organize sensory information from the environment. By providing specific sensory input through techniques like brushing, tapping, and vibration, the Rood approach helps in regulating sensory processing and improving sensory integration. This, in turn, enhances motor control by promoting the activation of specific muscle groups and facilitating coordinated movements. The Rood approach recognizes the close relationship between sensory integration and motor control and utilizes this connection to optimize functional outcomes.
The Rood approach employs various techniques to facilitate movement. Some common techniques used include tapping, brushing, vibration, and joint compression. Tapping involves rhythmic tapping on the muscles or tendons to elicit a muscle contraction response. Brushing refers to the use of a soft brush to stimulate the skin and enhance sensory input. Vibration can be applied using a vibrating tool or device to promote muscle activation and relaxation. Joint compression involves applying pressure to the joints to provide proprioceptive input and improve stability. These techniques are tailored to the individual's specific needs and goals, and they help in facilitating movement and enhancing motor control.
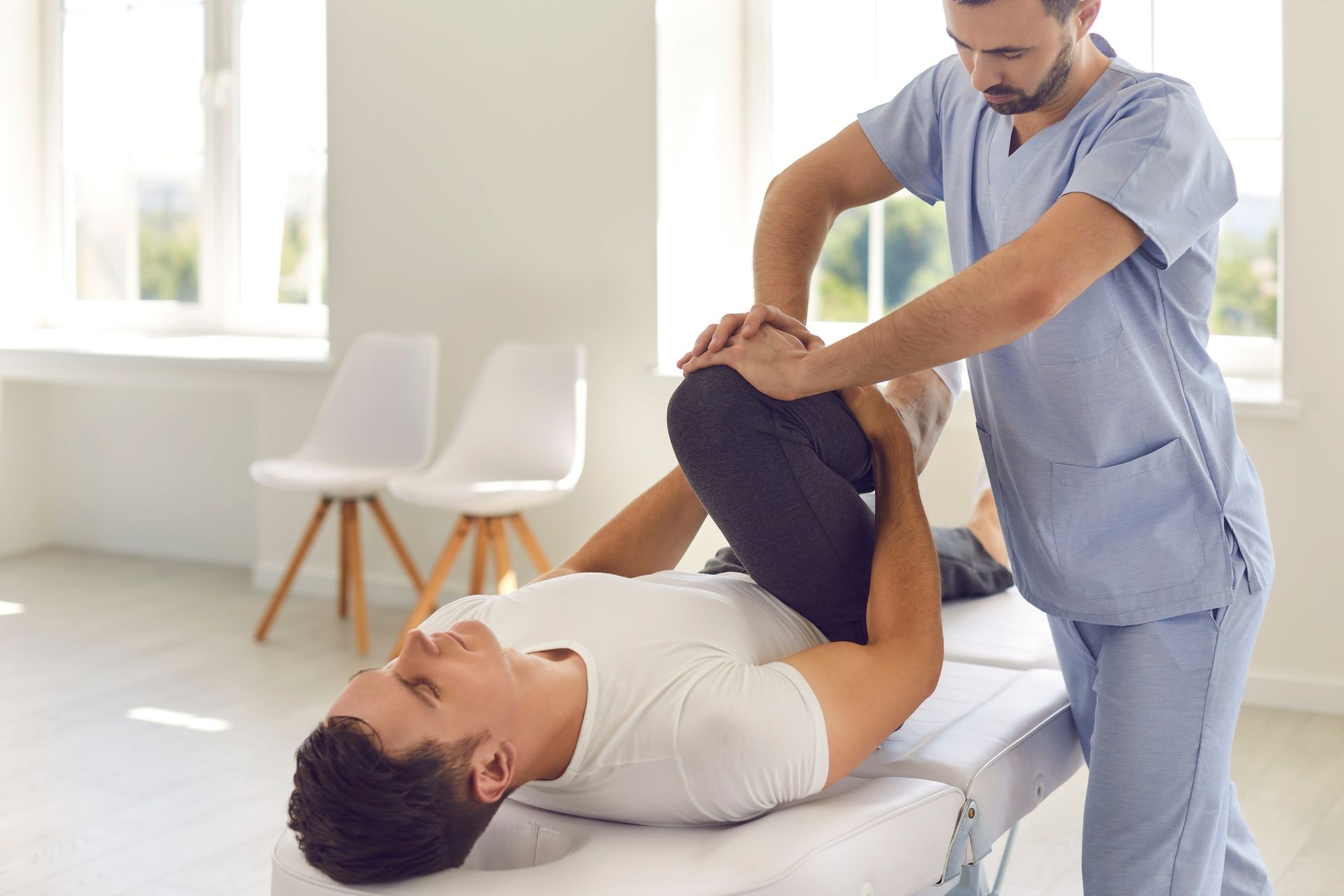
The Rood approach is particularly beneficial in the treatment of neurological conditions. Neurological conditions often result in motor impairments, such as muscle weakness, spasticity, and coordination difficulties. The Rood approach addresses these impairments by utilizing sensory stimulation techniques to activate specific muscle groups and improve motor control. By providing sensory input and facilitating appropriate motor responses, this approach can help individuals with neurological conditions regain functional abilities and improve their overall quality of life. The Rood approach is widely used in the rehabilitation of conditions such as stroke, traumatic brain injury, cerebral palsy, and multiple sclerosis.
While the Rood approach offers numerous benefits, there are some limitations and potential risks associated with its use. One limitation is that the effectiveness of the Rood approach may vary depending on the individual's specific condition and needs. It may not be suitable for everyone, and alternative approaches may be more appropriate in certain cases. Additionally, the Rood approach requires skilled and knowledgeable therapists who are trained in its principles and techniques. Without proper training and expertise, the application of the Rood approach may not yield optimal results. Furthermore, there is a potential risk of overstimulation or discomfort during the sensory stimulation techniques used in this approach. It is important for therapists to carefully monitor and adjust the intensity of the sensory input to ensure the safety and comfort of the individual undergoing treatment.

Manual lymphatic drainage techniques can be an effective method for managing lymphedema that occurs as a result of cancer treatment. Lymphedema is a condition characterized by the accumulation of lymph fluid in the tissues, typically in the arms or legs, due to damage or blockage of the lymphatic system. Cancer treatment, such as surgery or radiation therapy, can disrupt the normal flow of lymph fluid, leading to the development of lymphedema. Manual lymphatic drainage techniques involve gentle, rhythmic movements that stimulate the lymphatic system and encourage the drainage of excess fluid. These techniques, which may include specialized massage, compression bandaging, and exercise, can help reduce swelling, improve circulation, and alleviate discomfort associated with lymphedema. Additionally, manual lymphatic drainage techniques can promote the regeneration of lymphatic vessels and enhance the overall functioning of the lymphatic system. Therefore, incorporating manual lymphatic drainage techniques into a comprehensive treatment plan can be beneficial for individuals managing lymphedema following cancer treatment.
Proprioceptive insoles have been shown to have a positive impact on balance and gait stability in elderly patients. These insoles, which are designed to provide sensory feedback to the feet, can help improve proprioception, which is the body's ability to sense its position and movement in space. By enhancing proprioception, the insoles can help elderly patients maintain better balance and stability while walking. This can be particularly beneficial for individuals who may have age-related declines in proprioceptive function. Studies have demonstrated that the use of proprioceptive insoles can lead to improvements in gait parameters such as step length, stride width, and walking speed. Additionally, these insoles have been found to reduce the risk of falls in elderly individuals, which is a major concern for this population. Overall, proprioceptive insoles offer a promising intervention for enhancing balance and gait stability in elderly patients.
Therapists employ a comprehensive approach to tailor rehabilitation programs for individuals with Parkinson's disease, taking into account the unique needs and challenges faced by each patient. They begin by conducting a thorough assessment of the individual's physical abilities, cognitive function, and overall health status. This assessment helps therapists identify specific areas of impairment and determine the most appropriate interventions. Rehabilitation programs for Parkinson's disease typically include a combination of physical therapy, occupational therapy, and speech therapy. Physical therapy focuses on improving mobility, balance, and coordination through exercises and activities that target specific muscle groups. Occupational therapy aims to enhance the individual's ability to perform daily activities and maintain independence by addressing issues related to fine motor skills, self-care, and home modifications. Speech therapy addresses speech and swallowing difficulties commonly associated with Parkinson's disease. Additionally, therapists may incorporate other interventions such as cognitive training, assistive devices, and education on energy conservation techniques. The tailored rehabilitation programs are regularly reassessed and adjusted based on the individual's progress and changing needs, ensuring optimal outcomes and improved quality of life.
Open and closed kinetic chain exercises are two different approaches to knee rehabilitation. In open kinetic chain exercises, the distal segment of the limb is free to move, while in closed kinetic chain exercises, the distal segment is fixed or in contact with a stable surface. Open kinetic chain exercises typically involve isolated movements of the knee joint, such as leg extensions or hamstring curls, which target specific muscles. These exercises allow for greater control and precision in targeting specific muscle groups. On the other hand, closed kinetic chain exercises, such as squats or lunges, involve multiple joints and muscle groups working together. These exercises provide a more functional and dynamic approach to knee rehabilitation, as they mimic real-life movements and engage the entire lower extremity. Closed kinetic chain exercises also tend to place less stress on the knee joint and promote better joint stability. Both types of exercises have their benefits and can be used in combination to optimize knee rehabilitation outcomes.
Potential risks associated with instrument-assisted soft tissue mobilization (IASTM) techniques include bruising, skin irritation, and potential exacerbation of underlying conditions such as inflammation or infection. Improper use of the tools or excessive pressure during the technique can lead to tissue damage or nerve injury. Additionally, if the practitioner is not properly trained in IASTM, there is a risk of causing harm to the patient. It is important for practitioners to thoroughly assess the patient's medical history and current condition before performing IASTM to minimize the risk of complications. Furthermore, patients with certain medical conditions such as blood clotting disorders or compromised skin integrity may not be suitable candidates for IASTM due to the increased risk of adverse effects.