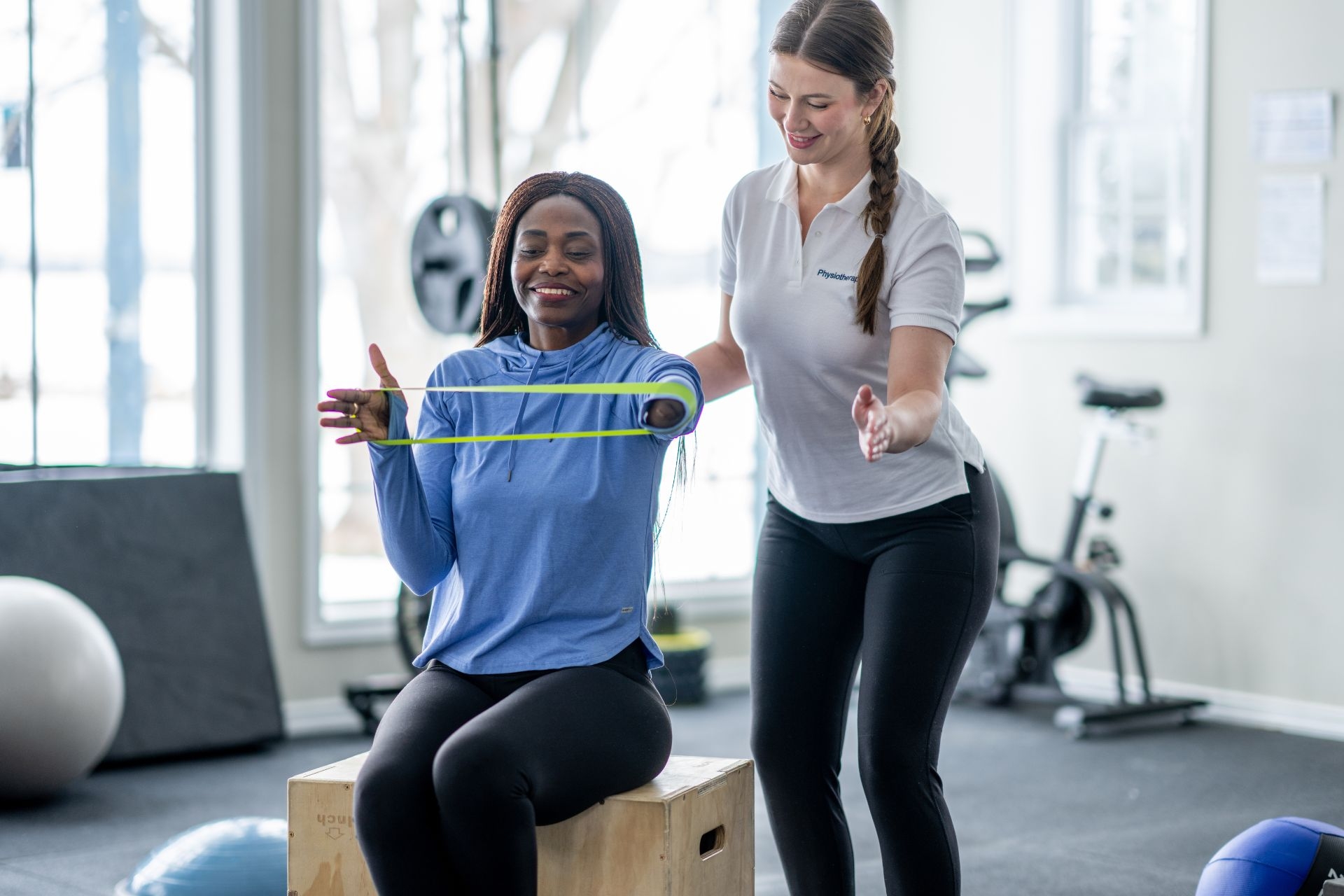


A Functional Capacity Evaluation (FCE) is a comprehensive assessment that evaluates an individual's physical abilities and limitations. It is conducted to determine a person's functional capacity to perform specific tasks, such as work-related activities. The evaluation is typically performed by a licensed healthcare professional, such as a physical therapist or occupational therapist, and involves a series of tests and measurements to assess the individual's strength, endurance, range of motion, and other physical abilities.
The main components of a Functional Capacity Evaluation include a thorough medical history review, physical examination, and functional testing. The medical history review involves gathering information about the individual's medical conditions, previous injuries, and current medications. The physical examination assesses the individual's range of motion, strength, and flexibility. Functional testing involves evaluating the individual's ability to perform specific tasks, such as lifting, carrying, pushing, and pulling.
Golf is often perceived as a leisurely activity, yet every time you take a shot, you’re engaging the hips, back, legs and arms. The repetition of gripping and swinging a golf club, coupled with potentially poor form, can place significant strain on these areas of the body. Learn about common golf injuries and prevention tactics... The post Common Golf Injuries appeared first on Integrated Rehabilitation Services.

Posted by on 2023-10-20
A Functional Capacity Evaluation is different from a regular physical examination in that it is specifically designed to assess an individual's ability to perform work-related tasks. While a regular physical examination may focus on identifying medical conditions or injuries, an FCE evaluates an individual's physical abilities and limitations in relation to their job requirements.
Standard PT Rehab Techniques To Ask Your Physical Therapist About
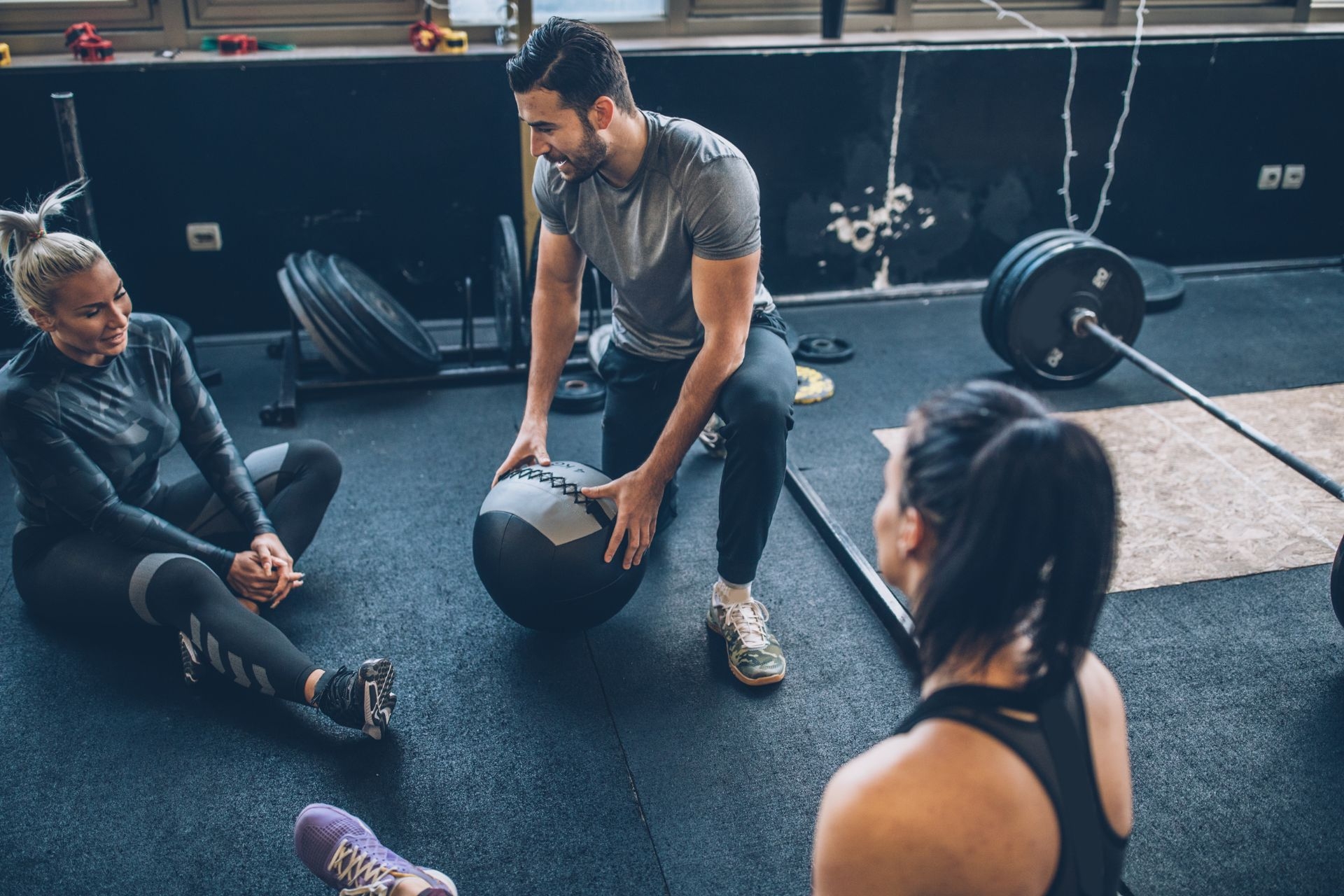

The common reasons for conducting a Functional Capacity Evaluation include determining an individual's ability to return to work after an injury or illness, assessing an individual's ability to perform specific job tasks, and evaluating an individual's need for accommodations or modifications in the workplace.
The potential benefits of undergoing a Functional Capacity Evaluation include gaining a better understanding of one's physical abilities and limitations, receiving recommendations for accommodations or modifications in the workplace, and improving the likelihood of a successful return to work after an injury or illness.
The potential limitations or risks associated with a Functional Capacity Evaluation include the possibility of exacerbating an existing injury or medical condition during the evaluation, as well as the potential for inaccurate results if the evaluation is not conducted properly.
The information gathered during a Functional Capacity Evaluation is used to determine an individual's ability to perform specific tasks or return to work. The results of the evaluation are typically used by healthcare professionals, employers, and insurance companies to make decisions about an individual's ability to work, the need for accommodations or modifications in the workplace, and the appropriate level of compensation for work-related injuries or illnesses.
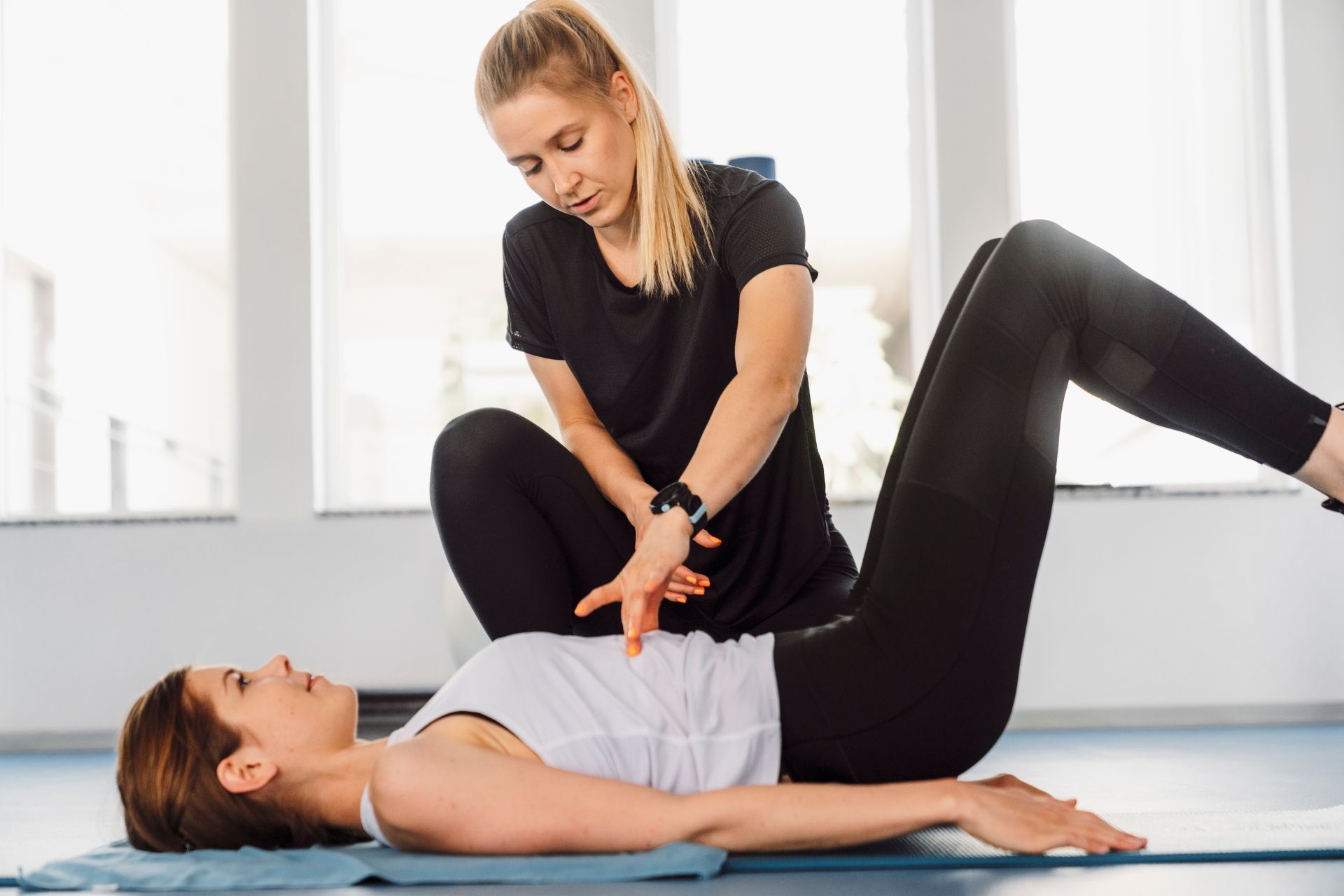

Individuals recovering from vestibular disorders can benefit from a variety of balance training exercises that target specific aspects of their condition. One effective exercise is the Romberg test, which involves standing with feet together and eyes closed to challenge proprioception and balance. Another beneficial exercise is the tandem walk, where the individual walks heel-to-toe in a straight line to improve coordination and stability. Additionally, the use of balance boards or stability balls can help improve balance and strengthen the core muscles. Other exercises that can be beneficial include single-leg stands, side-to-side weight shifts, and head movements to stimulate the vestibular system. It is important for individuals recovering from vestibular disorders to work with a healthcare professional to determine the most appropriate exercises for their specific condition and to ensure proper technique and safety.
Proprioceptive neuromuscular facilitation (PNF) is a stretching technique that differs from other stretching techniques in PT rehabilitation in several ways. PNF involves a combination of passive stretching and isometric contractions, which helps to increase flexibility and strength simultaneously. This technique also involves the use of proprioceptive feedback, which helps to improve body awareness and control. PNF is often used in PT rehabilitation to help patients recover from injuries or surgeries, as it can help to improve range of motion, reduce pain, and prevent further injury. Additionally, PNF can be customized to meet the specific needs of each patient, making it a highly effective and personalized form of rehabilitation. Overall, PNF is a unique and effective stretching technique that can help patients achieve their rehabilitation goals more quickly and effectively than other stretching techniques.
Physical therapists determine the appropriate resistance levels for isometric strengthening exercises in PT rehabilitation by conducting a thorough assessment of the patient's current strength, range of motion, and functional abilities. They may use tools such as dynamometers, hand-held dynamometers, or manual muscle testing to objectively measure the patient's strength and identify areas of weakness. Additionally, therapists take into account the patient's pain levels, medical history, and specific rehabilitation goals when determining the appropriate resistance levels for isometric exercises. By carefully monitoring the patient's progress and adjusting the resistance levels as needed, therapists can ensure that the exercises are challenging enough to promote strength gains, but not so difficult as to cause injury or exacerbate existing conditions. This individualized approach to resistance level determination helps optimize the effectiveness of the rehabilitation program and promotes safe and efficient recovery.
The Feldenkrais Method is a somatic approach to movement education that can be used to address chronic pain conditions such as fibromyalgia. This method focuses on improving body awareness and movement patterns through gentle, non-invasive movements. By increasing awareness of how the body moves and functions, individuals with fibromyalgia can learn to move in ways that reduce pain and discomfort. The Feldenkrais Method also emphasizes the importance of relaxation and reducing stress, which can be beneficial for managing fibromyalgia symptoms. Additionally, the method can help individuals with fibromyalgia improve their posture and alignment, which can reduce strain on the body and alleviate pain. Overall, the Feldenkrais Method offers a holistic approach to managing chronic pain conditions such as fibromyalgia.
Therapists can effectively integrate virtual reality technology into upper limb rehabilitation exercises by utilizing specialized software and hardware that provide immersive and interactive experiences. These systems often incorporate motion-tracking devices, such as sensors or cameras, to capture the patient's movements and translate them into the virtual environment. By incorporating haptic feedback devices, therapists can enhance the realism of the exercises and provide tactile sensations to the patient's upper limb. The virtual reality software can be programmed to offer a wide range of exercises and activities that target specific upper limb movements, such as reaching, grasping, and manipulating objects. Additionally, therapists can customize the difficulty level and intensity of the exercises to suit each patient's needs and progress. This integration of virtual reality technology not only adds an engaging and motivating element to the rehabilitation process but also allows therapists to track and analyze the patient's performance, providing valuable data for assessment and progress monitoring.
Aquatic therapy has been shown to provide significant benefits for individuals suffering from chronic lower back pain. The buoyancy of the water helps to reduce the impact on the joints and spine, allowing for gentle movement and exercise without exacerbating the pain. The hydrostatic pressure of the water also helps to decrease inflammation and swelling, providing relief to the affected area. Additionally, the resistance of the water provides a low-impact form of resistance training, which can help to strengthen the muscles supporting the lower back and improve overall stability. The warmth of the water can also help to relax muscles and increase blood flow, promoting healing and reducing pain. Overall, aquatic therapy offers a comprehensive approach to managing chronic lower back pain, addressing both the physical and psychological aspects of the condition.