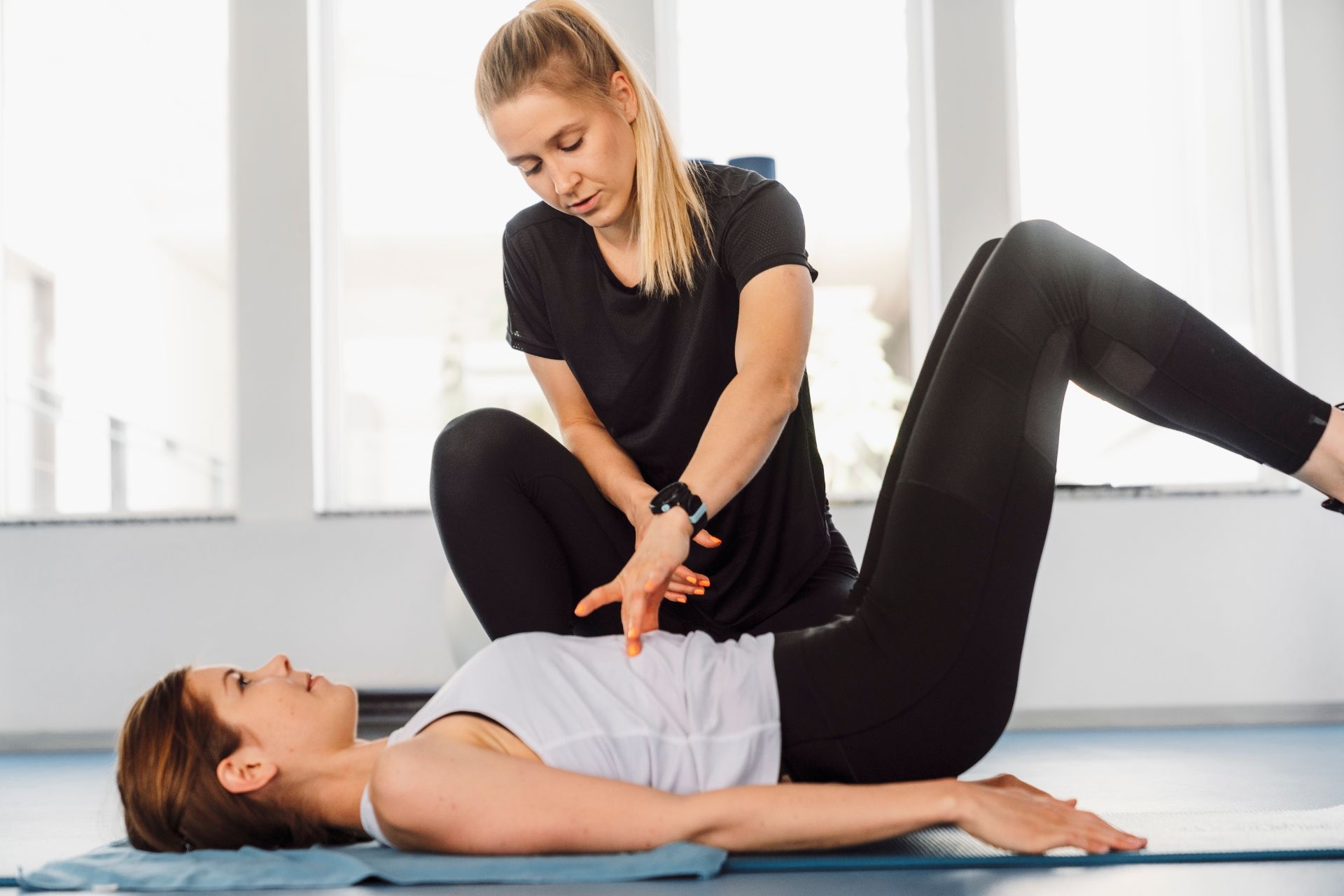


Redcord therapy helps improve core stability and balance by utilizing a unique suspension system that allows for targeted muscle activation. The therapy involves the use of slings and ropes to support the body while performing exercises, which creates an unstable environment. This instability forces the core muscles to engage in order to maintain balance and stability. By challenging the core muscles in this way, Redcord therapy helps to strengthen and stabilize the core, leading to improved balance and overall stability.
Standard PT Rehab Techniques To Ask Your Physical Therapist About
Redcord therapy utilizes a variety of exercises and techniques to target specific muscle groups. These exercises often involve the use of slings and ropes to create an unstable environment, which forces the targeted muscles to engage and stabilize the body. Some specific exercises used in Redcord therapy include plank variations, squats, lunges, and single-leg exercises. These exercises can be modified to target specific muscle groups, such as the core, glutes, or upper body. The therapy also incorporates neuromuscular activation techniques, which involve specific movements and positions to activate and strengthen specific muscles.
Throughout your body, tendons keep the muscles secure to the bones. Although tendons are built to handle significant force, factors like repeat wear and tear, certain diseases, steroid use or an untreated injury can cause this thick, fibrous tissue to tear or snap, resulting in a rupture. The risk of partial and full tendon tears... The post How Does a Ruptured Tendon Occur? appeared first on Integrated Rehabilitation Services.

Posted by on 2023-09-01
Redcord therapy can be used as a rehabilitation method for individuals with spinal cord injuries. The therapy's focus on core stability and balance can be particularly beneficial for individuals with spinal cord injuries, as these injuries often result in weakened core muscles and impaired balance. Redcord therapy can help to strengthen the core muscles, improve balance, and enhance overall functional ability. However, it is important for individuals with spinal cord injuries to work with a qualified therapist who can tailor the therapy to their specific needs and limitations.
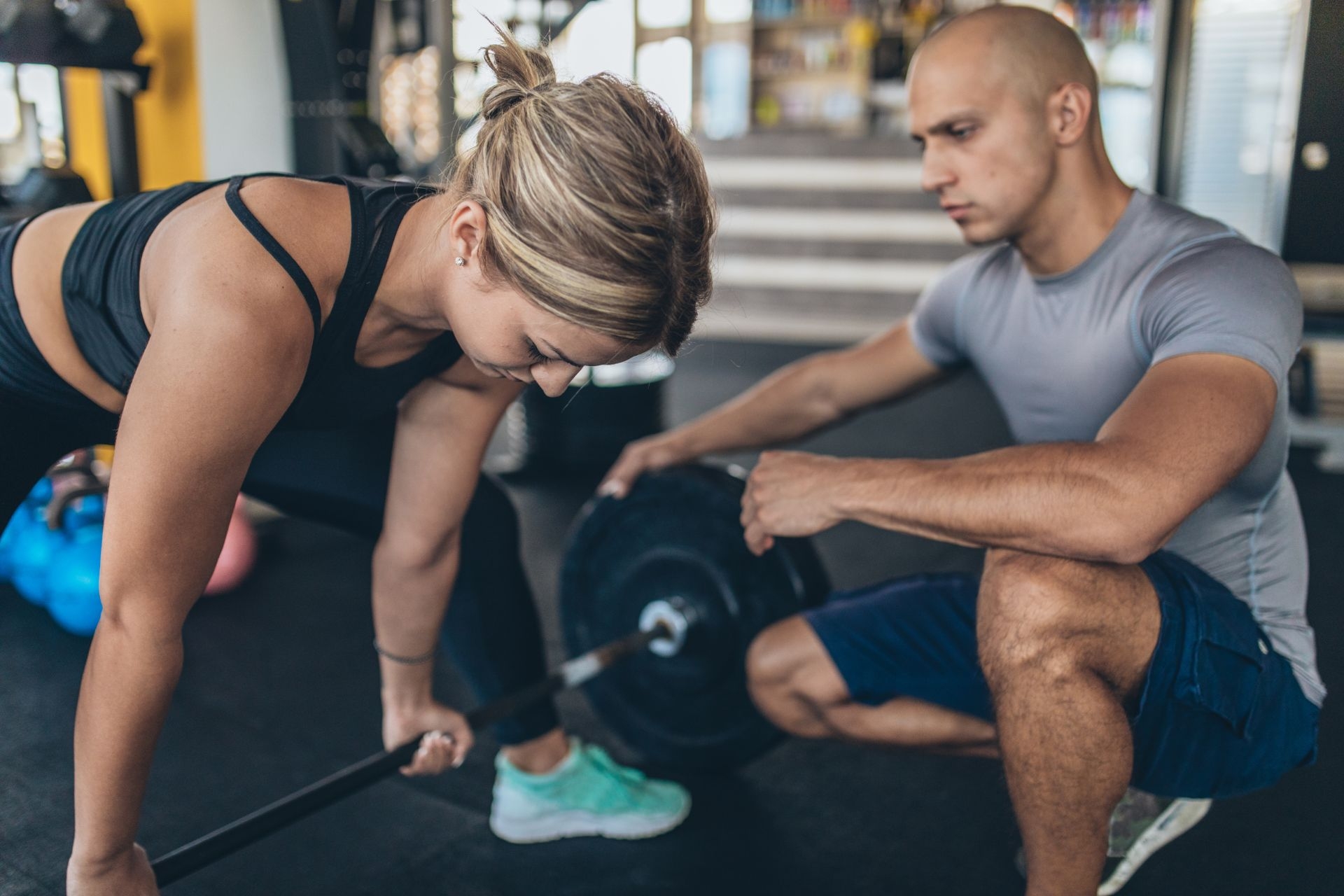

Redcord therapy differs from traditional physical therapy methods in several ways. Traditional physical therapy often focuses on isolated muscle strengthening exercises, while Redcord therapy emphasizes functional movements and whole-body integration. Redcord therapy also utilizes the suspension system to create an unstable environment, which challenges the core muscles and promotes neuromuscular activation. Additionally, Redcord therapy incorporates specific techniques and exercises that target deep stabilizing muscles, which are often overlooked in traditional physical therapy. Overall, Redcord therapy offers a unique and effective approach to improving core stability and balance.
Before starting Redcord therapy, there are some contraindications and precautions to consider. Individuals with certain medical conditions, such as uncontrolled hypertension, cardiovascular disease, or acute injuries, may not be suitable candidates for Redcord therapy. It is important to consult with a qualified therapist or healthcare professional to determine if Redcord therapy is appropriate for an individual's specific condition. Additionally, individuals should be aware that Redcord therapy can be physically demanding and may require a certain level of strength and stability to safely perform the exercises.
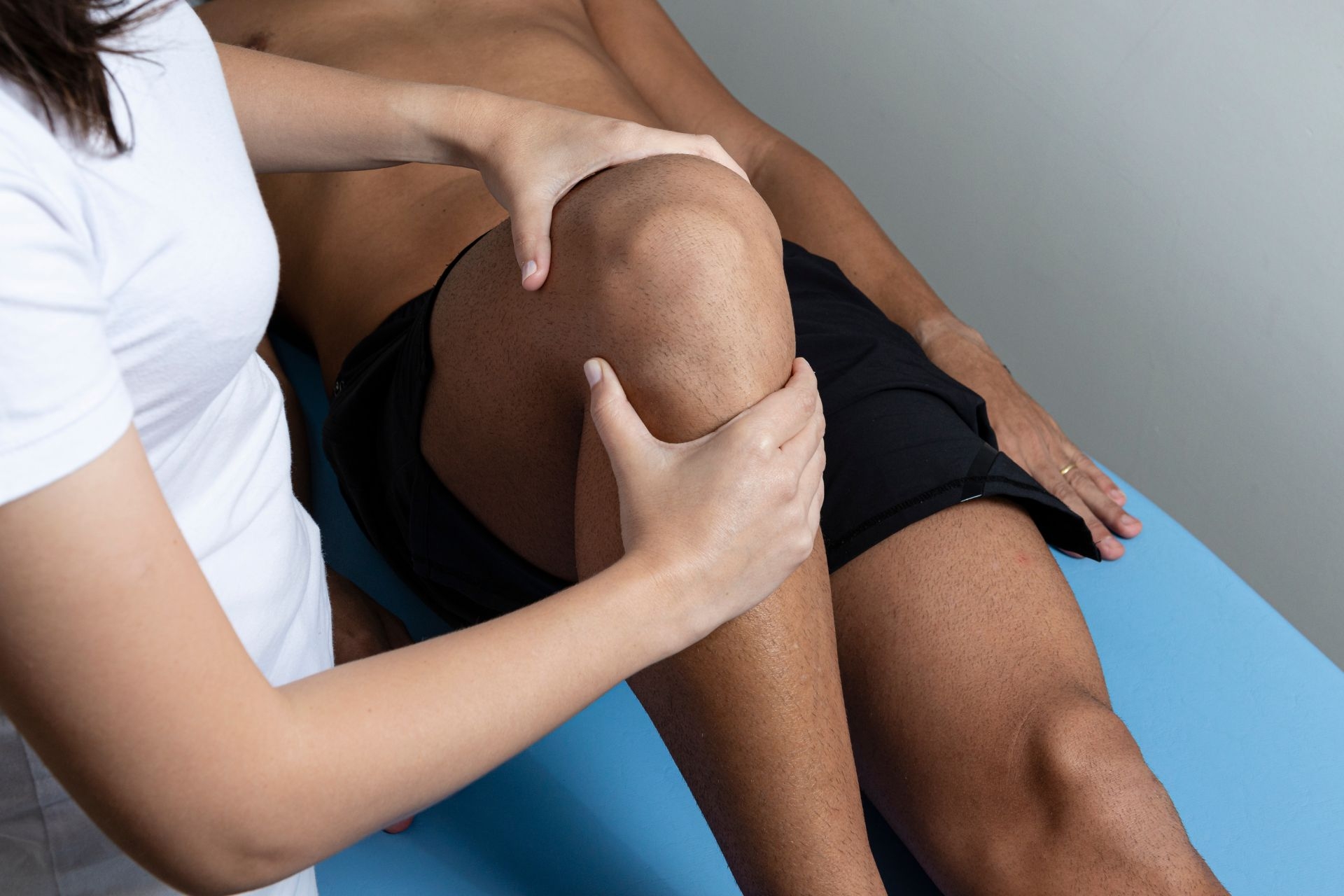
Yes, Redcord therapy can be used to improve athletic performance and prevent sports-related injuries. The therapy's focus on core stability, balance, and neuromuscular activation can help athletes enhance their overall strength, power, and coordination. By targeting specific muscle groups and challenging the body in an unstable environment, Redcord therapy can improve an athlete's ability to generate force, maintain proper alignment, and prevent injuries. It can also help athletes recover from injuries by strengthening the affected muscles and improving overall functional ability.
There is scientific evidence that supports the effectiveness of Redcord therapy in treating musculoskeletal conditions. Several studies have shown that Redcord therapy can improve core stability, balance, and functional ability in individuals with various musculoskeletal conditions, such as low back pain, shoulder impingement, and knee osteoarthritis. These studies have demonstrated improvements in muscle strength, pain reduction, and functional outcomes following Redcord therapy interventions. However, more research is needed to further validate the effectiveness of Redcord therapy and to explore its potential benefits for other musculoskeletal conditions.
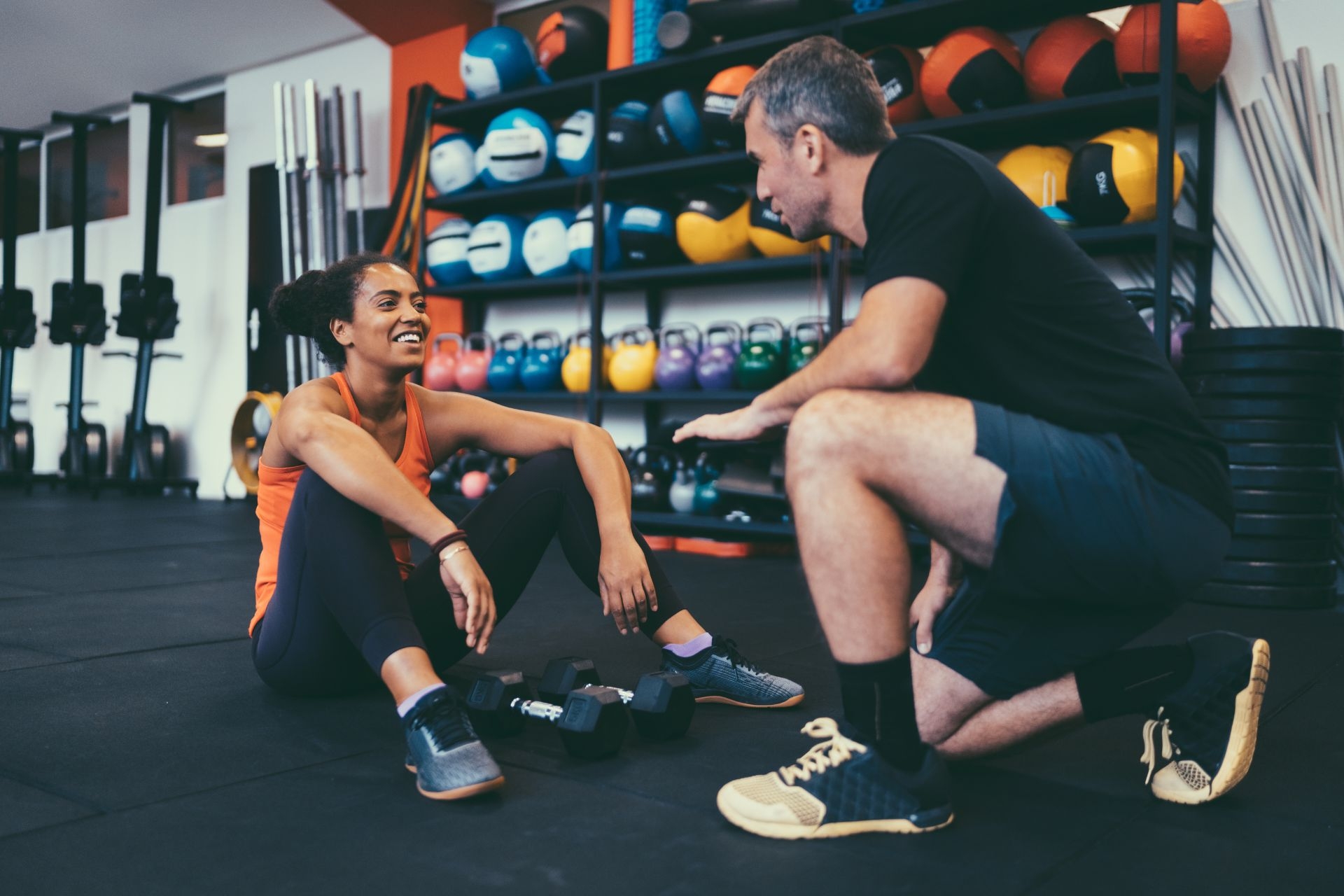

Therapists employ various assessment techniques to evaluate and treat muscle imbalances in shoulder rehabilitation programs. They may conduct a thorough physical examination to assess the range of motion, strength, and stability of the shoulder joint. This evaluation may involve specific tests such as the Hawkins-Kennedy test, Neer test, or Jobe test to identify any impingement or rotator cuff issues. Additionally, therapists may use electromyography (EMG) to measure muscle activity and identify any imbalances or weaknesses. Once the imbalances are identified, therapists can address them through a combination of targeted exercises, stretching, and manual therapy techniques. These interventions may include strengthening exercises for weak muscles, stretching exercises for tight muscles, and techniques such as myofascial release or joint mobilization to restore proper alignment and function. By addressing muscle imbalances, therapists aim to restore optimal shoulder function and prevent future injuries.
The Mulligan concept and Maitland approach are two different manual therapy techniques used in physical therapy rehabilitation. The key differences between these approaches lie in their underlying principles and treatment techniques. The Mulligan concept, developed by Brian Mulligan, focuses on the concept of mobilization with movement (MWM) and emphasizes the use of pain-free techniques to restore joint function and reduce pain. It involves the application of sustained glides or accessory movements to the joint while the patient performs specific active movements. On the other hand, the Maitland approach, developed by Geoffrey Maitland, is based on the principles of passive joint mobilization and graded oscillatory movements. It involves the therapist applying graded pressure and oscillatory movements to the joint to restore its range of motion and reduce pain. While both approaches aim to improve joint function and reduce pain, the Mulligan concept places more emphasis on active patient participation and pain-free techniques, whereas the Maitland approach focuses on passive joint mobilization and graded oscillatory movements.
Cupping therapy has been shown to influence tissue perfusion and pain modulation in physical therapy (PT) rehabilitation. The application of negative pressure through the use of cups can lead to increased blood flow, improved microcirculation, and enhanced tissue oxygenation, ultimately promoting tissue perfusion. This can result in accelerated healing, reduced inflammation, and improved tissue repair, which are all crucial components of the rehabilitation process. Additionally, cupping therapy has been found to stimulate the release of endorphins and other neuropeptides, leading to pain modulation and relief. By targeting trigger points and areas of pain, cupping therapy can help alleviate discomfort and improve overall function, making it a valuable adjunct to PT rehabilitation programs.
There are several psychological factors that can influence adherence to home exercise programs. One important factor is motivation, which can be influenced by a person's beliefs, values, and goals. For example, if someone believes that exercise is important for their overall health and has a goal of improving their fitness level, they may be more motivated to stick to their home exercise program. Another factor is self-efficacy, which refers to a person's belief in their ability to successfully complete a task. If someone has high self-efficacy for exercise, they are more likely to believe that they can successfully complete their home exercise program and are therefore more likely to adhere to it. Additionally, social support can play a role in adherence. Having support from friends, family, or a workout buddy can provide encouragement and accountability, making it more likely that a person will stick to their home exercise program. Finally, enjoyment of the exercise itself can also influence adherence. If someone finds their home exercise program enjoyable and engaging, they are more likely to continue with it over time.
Individuals with hypermobility syndromes require exercise programs that are tailored to their specific needs. Therapists modify exercise programs by focusing on stability and strengthening exercises that target the muscles surrounding the hypermobile joints. These exercises aim to improve joint stability and reduce the risk of injury. Therapists also incorporate low-impact exercises, such as swimming or cycling, to reduce the stress on the joints. Additionally, therapists may use props, such as resistance bands or stability balls, to provide additional support during exercises. It is important for therapists to monitor the individual's progress and adjust the exercise program accordingly to ensure that it is effective and safe.
Neurodynamic techniques, such as nerve flossing, tensioning, and sliders, have been shown to be effective in the management of sciatic nerve pain. These techniques involve specific movements and stretches that aim to mobilize and desensitize the sciatic nerve and its surrounding tissues. By addressing neural tension and improving nerve mobility, neurodynamic techniques can help alleviate symptoms associated with sciatic nerve pain, such as radiating leg pain, numbness, and tingling. Additionally, incorporating neurodynamic techniques into a comprehensive treatment plan for sciatic nerve pain may also help improve flexibility, reduce muscle tension, and enhance overall functional mobility. Overall, the use of neurodynamic techniques can be a valuable component in the holistic management of sciatic nerve pain.
The McKenzie Method is commonly used in the treatment of lumbar disc herniation due to its effectiveness in reducing pain and improving function. Indications for using this method include patients experiencing radicular pain, such as sciatica, which is caused by the compression of a nerve root due to the herniated disc. Additionally, patients with symptoms of numbness, tingling, or weakness in the lower extremities may benefit from this treatment approach. The McKenzie Method is also suitable for individuals with a history of recurrent or chronic low back pain, as it aims to address the underlying mechanical dysfunction and promote self-management strategies. Furthermore, patients who prefer a non-invasive and conservative treatment option may find the McKenzie Method appealing, as it focuses on active patient participation through specific exercises and postural modifications.