
Isometric exercises are a great way to improve muscle strength. These exercises involve holding a static position, which causes the muscles to contract without any movement. This type of exercise is particularly effective for building strength in the muscles that are used to hold the body in place, such as the core, back, and legs. Isometric exercises can also be used to target specific muscle groups, making them a versatile option for anyone looking to improve their overall strength.
Isometric exercises differ from traditional strength training exercises in that they do not involve any movement. Instead, the muscles are contracted and held in a static position for a period of time. This type of exercise is particularly effective for building strength in the muscles that are used to hold the body in place, such as the core, back, and legs. Isometric exercises can also be used to target specific muscle groups, making them a versatile option for anyone looking to improve their overall strength.
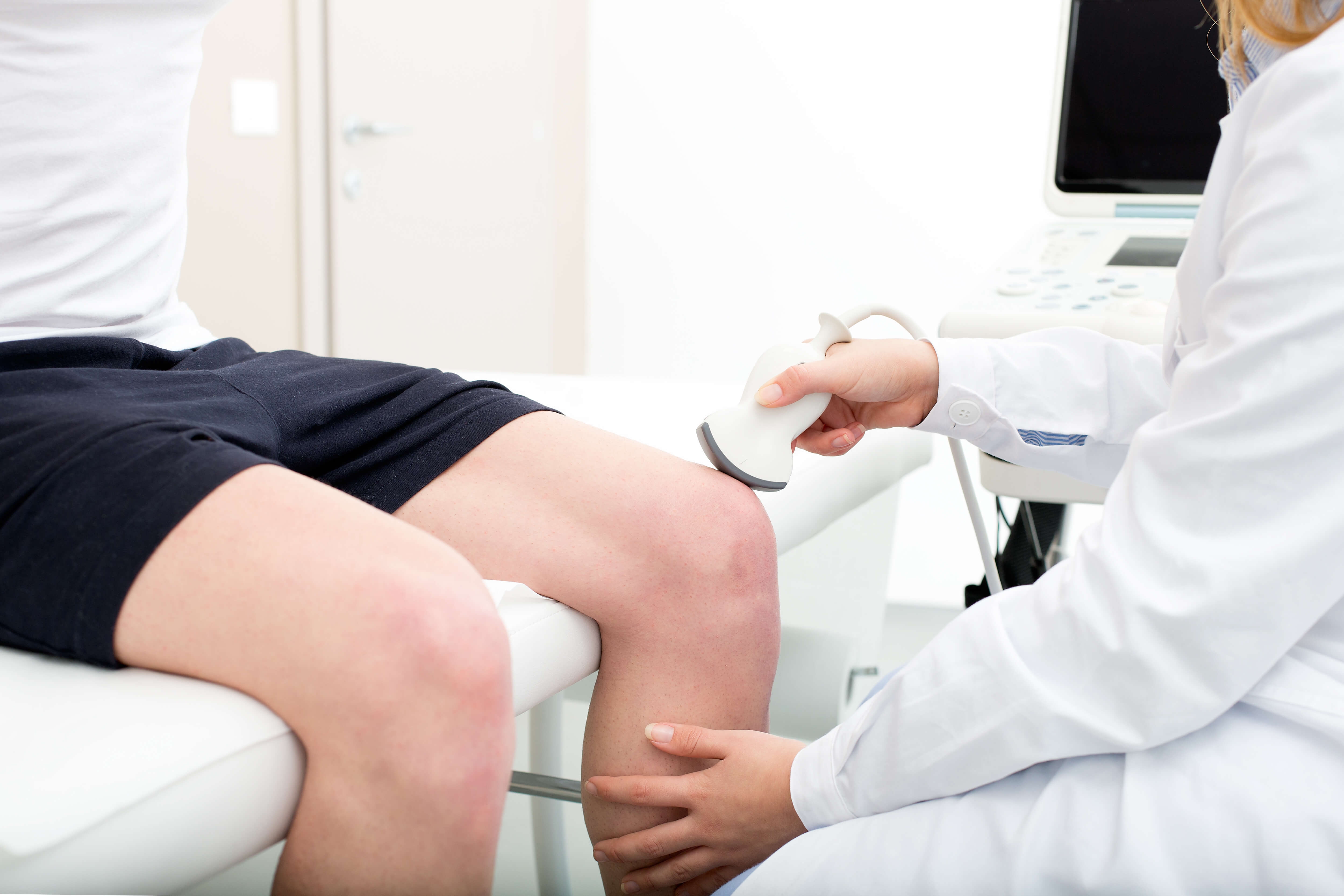
The hip is one of the body’s largest and most stable joints. Intended for a wider range of motion, this ball-and-socket-style joint bears a significant amount of weight. It’s also surrounded by various ligaments, tendons and soft tissues for support. An injury to this area can affect your mobility on a broader scale and often... The post Common Types of Hip Injuries appeared first on Integrated Rehabilitation Services.

Posted by on 2023-12-14
As you grow older, your body goes through many changes. These factors not only affect its functionality but can make you more vulnerable to falls and certain chronic conditions. Geriatric physical therapy addresses these needs for patients 65 and older, including injury recovery and prevention. If you are within this age group and your doctor... The post What to Expect During Physical Therapy for Seniors appeared first on Integrated Rehabilitation Services.

Posted by on 2023-12-07
After a serious injury, surgery and recovery can take a toll on the body. Regaining muscle strength can be an uphill battle of slow, incremental progress to reach the level and skill once attained. Blood flow restriction therapy (BFR) partially interrupts this process to aid recovery without greatly impacting muscle strength. Learn more about this... The post Blood Flow Restriction Therapy for Injury Recovery appeared first on Integrated Rehabilitation Services.

Posted by on 2023-10-31
Golf is often perceived as a leisurely activity, yet every time you take a shot, you’re engaging the hips, back, legs and arms. The repetition of gripping and swinging a golf club, coupled with potentially poor form, can place significant strain on these areas of the body. Learn about common golf injuries and prevention tactics... The post Common Golf Injuries appeared first on Integrated Rehabilitation Services.

Posted by on 2023-10-20
Isometric exercises can help improve flexibility and range of motion. By holding a static position, the muscles are stretched and lengthened, which can help improve flexibility over time. This type of exercise is particularly effective for improving flexibility in the muscles that are used to hold the body in place, such as the core, back, and legs. Isometric exercises can also be used to target specific muscle groups, making them a versatile option for anyone looking to improve their overall flexibility.
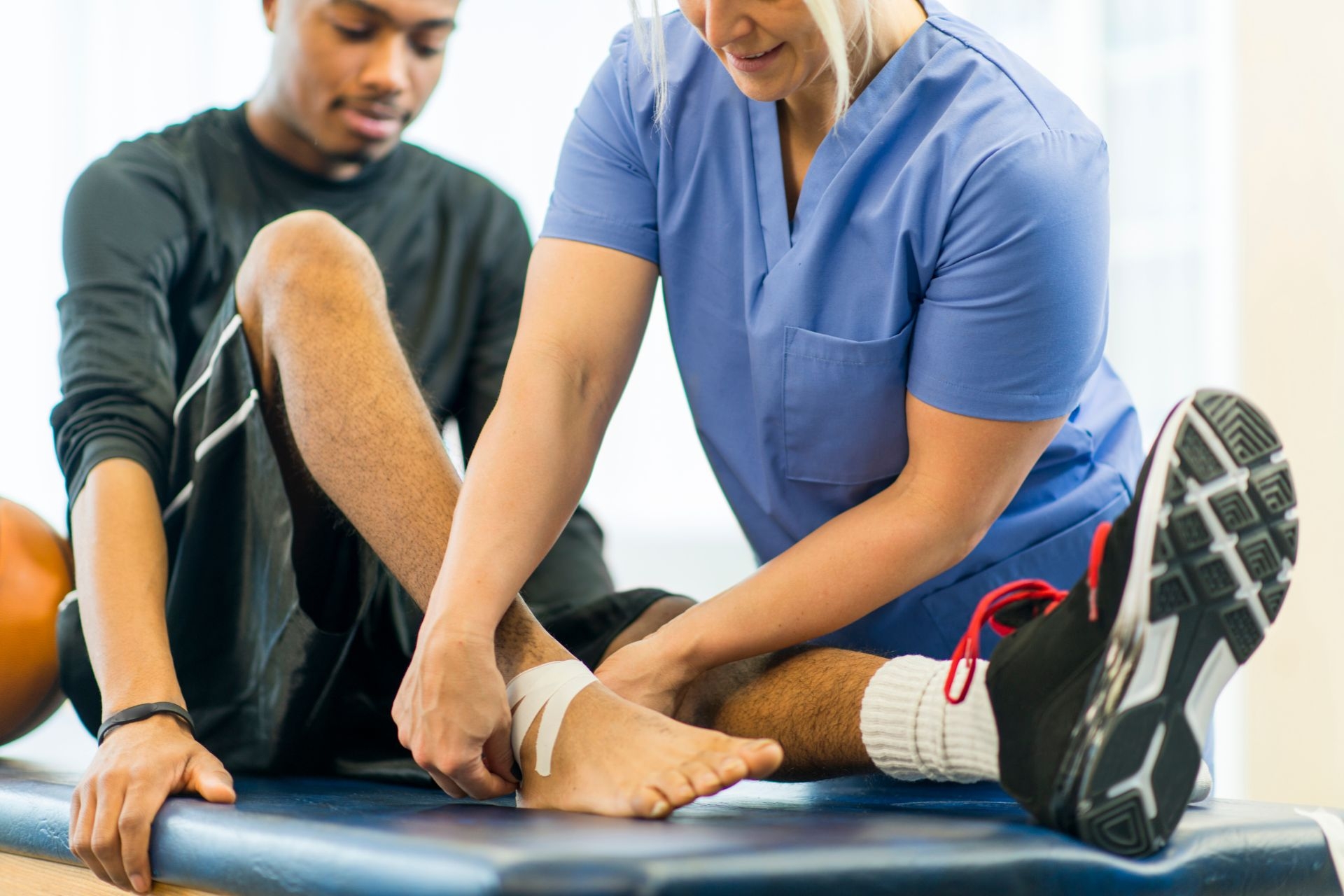
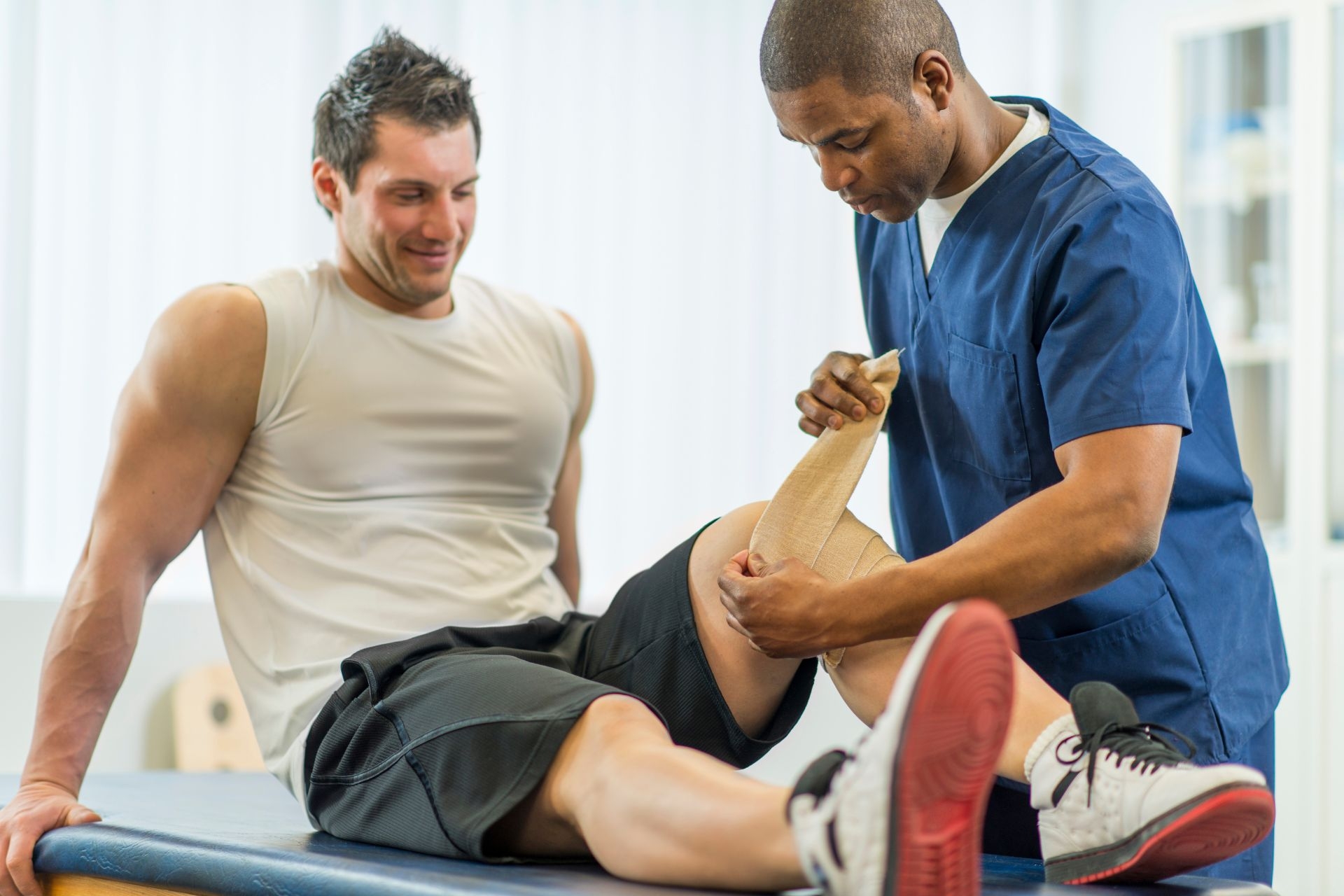
Standard PT Rehab Techniques To Ask Your Physical Therapist About
Isometric exercises can be suitable for individuals with joint problems or injuries. Because these exercises do not involve any movement, they can be less stressful on the joints than traditional strength training exercises. However, it is important to consult with a doctor or physical therapist before starting any new exercise program, especially if you have a history of joint problems or injuries.
There are many examples of isometric exercises that target specific muscle groups. For example, a plank is an isometric exercise that targets the core muscles. To perform a plank, start in a push-up position and then lower your body down so that your forearms are resting on the ground. Hold this position for as long as you can. Other examples of isometric exercises include wall sits, glute bridges, and calf raises.
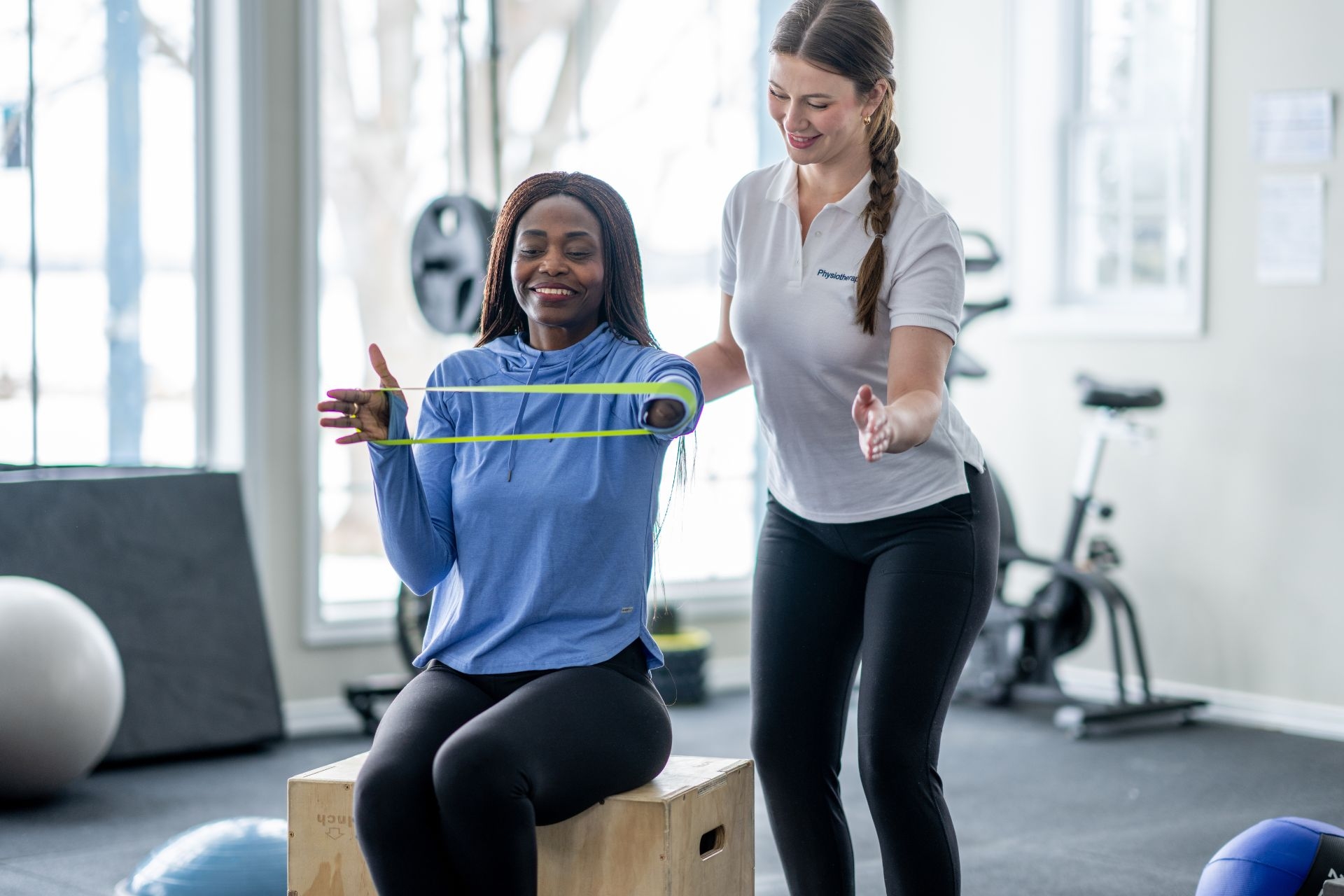

The length of time that one should hold an isometric exercise position to see results can vary depending on the individual and the specific exercise being performed. Generally, it is recommended to hold the position for at least 10-30 seconds, and then gradually increase the time as your strength improves. It is important to listen to your body and not push yourself too hard, as this can lead to injury.
Isometric exercises can be incorporated into a cardiovascular workout routine. For example, you could perform a set of isometric exercises in between running or cycling intervals. This can help improve overall strength and endurance, while also providing a break from the high-intensity cardio. Isometric exercises can also be used as a warm-up or cool-down before or after a cardio workout.
Several studies have provided evidence supporting the use of Pilates-based rehabilitation for improving core stability. A systematic review conducted by Smith et al. (2015) found that Pilates exercises significantly improved core stability in healthy individuals and those with low back pain. Another study by Wells et al. (2012) demonstrated that Pilates-based rehabilitation was effective in improving core stability and reducing pain in individuals with chronic low back pain. Additionally, a randomized controlled trial by Rydeard et al. (2006) showed that Pilates exercises improved core stability and reduced disability in patients with non-specific low back pain. These findings suggest that Pilates-based rehabilitation can be an effective intervention for enhancing core stability in various populations.
When prescribing therapeutic ultrasound for tendonitis rehabilitation, there are several key considerations that need to be taken into account. Firstly, the therapist should assess the severity and stage of the tendonitis to determine the appropriate treatment protocol. This may involve considering factors such as the location of the tendonitis, the extent of inflammation, and the presence of any underlying conditions. Additionally, the therapist should consider the patient's individual characteristics, such as their age, overall health, and tolerance to ultrasound therapy. It is also important to consider the specific goals of the rehabilitation program and how ultrasound can be integrated into a comprehensive treatment plan. Furthermore, the therapist should be knowledgeable about the different ultrasound parameters, such as frequency, intensity, and treatment duration, and how they can be adjusted to optimize the therapeutic effects. Finally, regular monitoring and reassessment of the patient's progress should be conducted to ensure that the ultrasound therapy is effective and appropriate adjustments can be made if necessary.
Acupuncture has been suggested as a potential treatment option for patients with temporomandibular joint disorders (TMDs) to improve functional outcomes. TMDs encompass a range of conditions affecting the jaw joint and surrounding muscles, leading to pain, limited jaw movement, and difficulty in performing daily activities such as eating and speaking. Research studies have explored the effects of acupuncture on TMDs, with some indicating positive outcomes in terms of pain reduction, improved jaw function, and increased quality of life. Acupuncture, a traditional Chinese medicine technique involving the insertion of thin needles at specific points on the body, is believed to stimulate the release of endorphins, modulate pain perception, and promote relaxation. Additionally, acupuncture may help alleviate muscle tension and inflammation, which are common features of TMDs. However, it is important to note that the evidence supporting the effectiveness of acupuncture for TMDs is still limited and further high-quality research is needed to establish its true efficacy.
The primary goals of plyometric training in post-ACL reconstruction rehabilitation are to improve neuromuscular control, enhance muscular power, increase functional performance, and reduce the risk of reinjury. Plyometric exercises involve rapid stretching and contracting of muscles, which helps to improve the coordination and timing of muscle activation. This type of training also helps to develop explosive power, which is important for activities that require quick and forceful movements, such as jumping and cutting. By incorporating plyometric exercises into the rehabilitation program, individuals can regain their ability to perform functional movements with confidence and reduce the likelihood of future ACL injuries.
Dry needling and acupuncture are both techniques used in physical therapy rehabilitation, but they differ in their approach and underlying principles. Dry needling involves the insertion of thin needles into trigger points or tight muscles to release tension and promote healing. It focuses on targeting specific areas of muscle dysfunction and stimulating a local twitch response to alleviate pain and improve muscle function. On the other hand, acupuncture is based on traditional Chinese medicine principles and involves the insertion of needles into specific points along meridians to restore the flow of energy or Qi in the body. It aims to rebalance the body's energy and promote overall well-being. While both techniques involve the use of needles, dry needling is more focused on musculoskeletal issues and is often used in conjunction with other physical therapy interventions, whereas acupuncture has a broader scope and is used to address a wide range of conditions beyond musculoskeletal problems.
Individuals with plantar fasciitis can benefit from incorporating specific stretching techniques into their daily routine. One effective technique is the calf stretch, which involves standing facing a wall and placing one foot forward while keeping the other foot back. The individual can then lean forward, keeping their back leg straight and their heel on the ground, until they feel a stretch in their calf. Another helpful stretch is the towel stretch, where the person sits on the floor with their legs straight out in front of them and loops a towel around the ball of their foot. They can then gently pull the towel towards them, stretching the plantar fascia. Additionally, the seated plantar fascia stretch can be beneficial. This involves sitting in a chair and crossing one leg over the other, then gently pulling the toes back towards the shin until a stretch is felt in the arch of the foot. These stretching techniques can help alleviate the symptoms of plantar fasciitis by improving flexibility and reducing tension in the affected area.