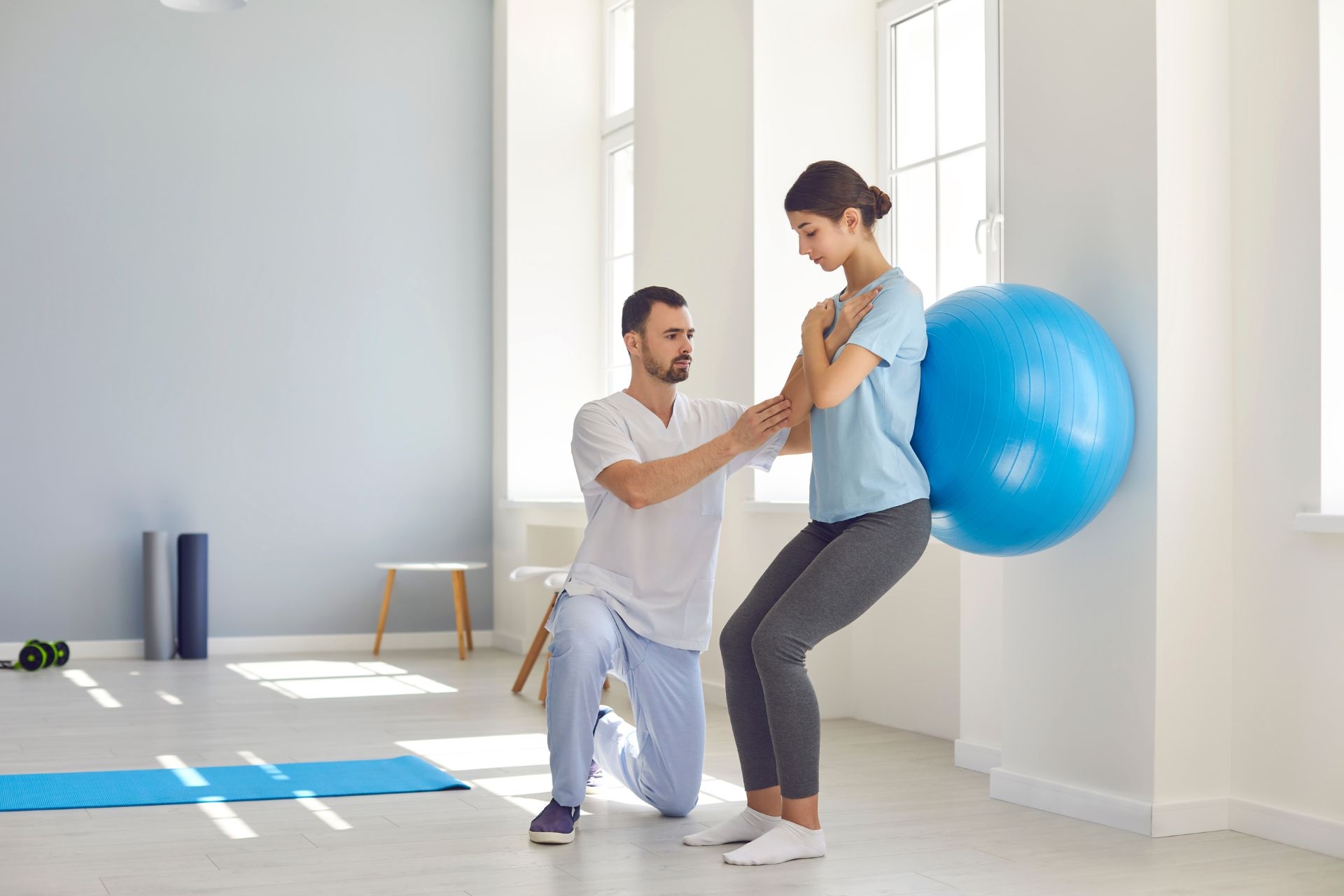


There are several exercises that are specifically designed to correct posture. One such exercise is the wall angel exercise, where you stand with your back against a wall and slowly raise your arms up and down while keeping your back and head in contact with the wall. Another exercise is the shoulder blade squeeze, where you sit or stand with your arms by your sides and squeeze your shoulder blades together, holding for a few seconds before releasing. Additionally, exercises such as planks, bird dogs, and bridges can also help strengthen the core and back muscles, which are important for maintaining good posture.
Standard PT Rehab Techniques To Ask Your Physical Therapist About
Stretching exercises can be beneficial for improving posture by increasing flexibility and relieving muscle tension. One effective stretch is the chest stretch, where you stand in a doorway with your arms outstretched and place your hands on the door frame, then lean forward to feel a stretch in your chest and shoulders. Another stretch is the upper trapezius stretch, where you sit or stand with one hand behind your back and gently tilt your head to the opposite side, feeling a stretch in the side of your neck. Stretching the hip flexors and hamstrings can also help improve posture by reducing tightness in these areas.
Golf is often perceived as a leisurely activity, yet every time you take a shot, you’re engaging the hips, back, legs and arms. The repetition of gripping and swinging a golf club, coupled with potentially poor form, can place significant strain on these areas of the body. Learn about common golf injuries and prevention tactics... The post Common Golf Injuries appeared first on Integrated Rehabilitation Services.

Posted by on 2023-10-20
Throughout your body, tendons keep the muscles secure to the bones. Although tendons are built to handle significant force, factors like repeat wear and tear, certain diseases, steroid use or an untreated injury can cause this thick, fibrous tissue to tear or snap, resulting in a rupture. The risk of partial and full tendon tears... The post How Does a Ruptured Tendon Occur? appeared first on Integrated Rehabilitation Services.

Posted by on 2023-09-01
There are specific exercises that target the muscles responsible for maintaining good posture. These exercises focus on strengthening the core, back, and shoulder muscles. For example, exercises such as rows, lat pulldowns, and reverse flys target the muscles in the upper back and shoulders. Planks and side planks are effective for strengthening the core muscles, while exercises like supermans and bridges target the muscles in the lower back. By regularly performing these exercises, individuals can strengthen the muscles necessary for maintaining proper posture.

One common mistake people make when trying to correct their posture through exercise is focusing solely on strengthening the muscles in the back and neglecting the core muscles. It is important to have a strong core to support the spine and maintain good posture. Another mistake is performing exercises with incorrect form, which can lead to injury or ineffective results. It is crucial to maintain proper alignment and engage the correct muscles during each exercise. Additionally, some individuals may try to correct their posture too quickly, which can be overwhelming for the body. Gradual progress and consistency are key when it comes to improving posture through exercise.
Yes, both yoga and Pilates can help improve posture. These practices focus on strengthening the core, improving flexibility, and promoting body awareness, all of which are important for maintaining good posture. Yoga poses such as mountain pose, tree pose, and cat-cow pose can help align the spine and improve posture. Pilates exercises, such as the hundred, roll-up, and shoulder bridge, target the core and back muscles, which are essential for proper posture. Regular practice of yoga or Pilates can lead to improved posture and overall body alignment.
There are exercises that can be done at a desk to improve posture. One exercise is the seated back extension, where you sit upright in your chair and place your hands on the back of your head. Gently lean back, keeping your back straight, and then return to the starting position. Another exercise is the seated shoulder blade squeeze, where you sit with your arms by your sides and squeeze your shoulder blades together, holding for a few seconds before releasing. Additionally, taking breaks to stand up, stretch, and walk around can also help improve posture and prevent stiffness from prolonged sitting.
The time it takes to see improvements in posture through exercise can vary depending on several factors, including the individual's current posture, consistency of exercise, and the specific exercises performed. Generally, it may take several weeks to a few months of regular exercise to notice significant improvements in posture. Consistency is key, as regular practice of exercises that target the muscles responsible for maintaining good posture can gradually strengthen and align the body. It is important to be patient and persistent in order to see long-lasting improvements in posture.
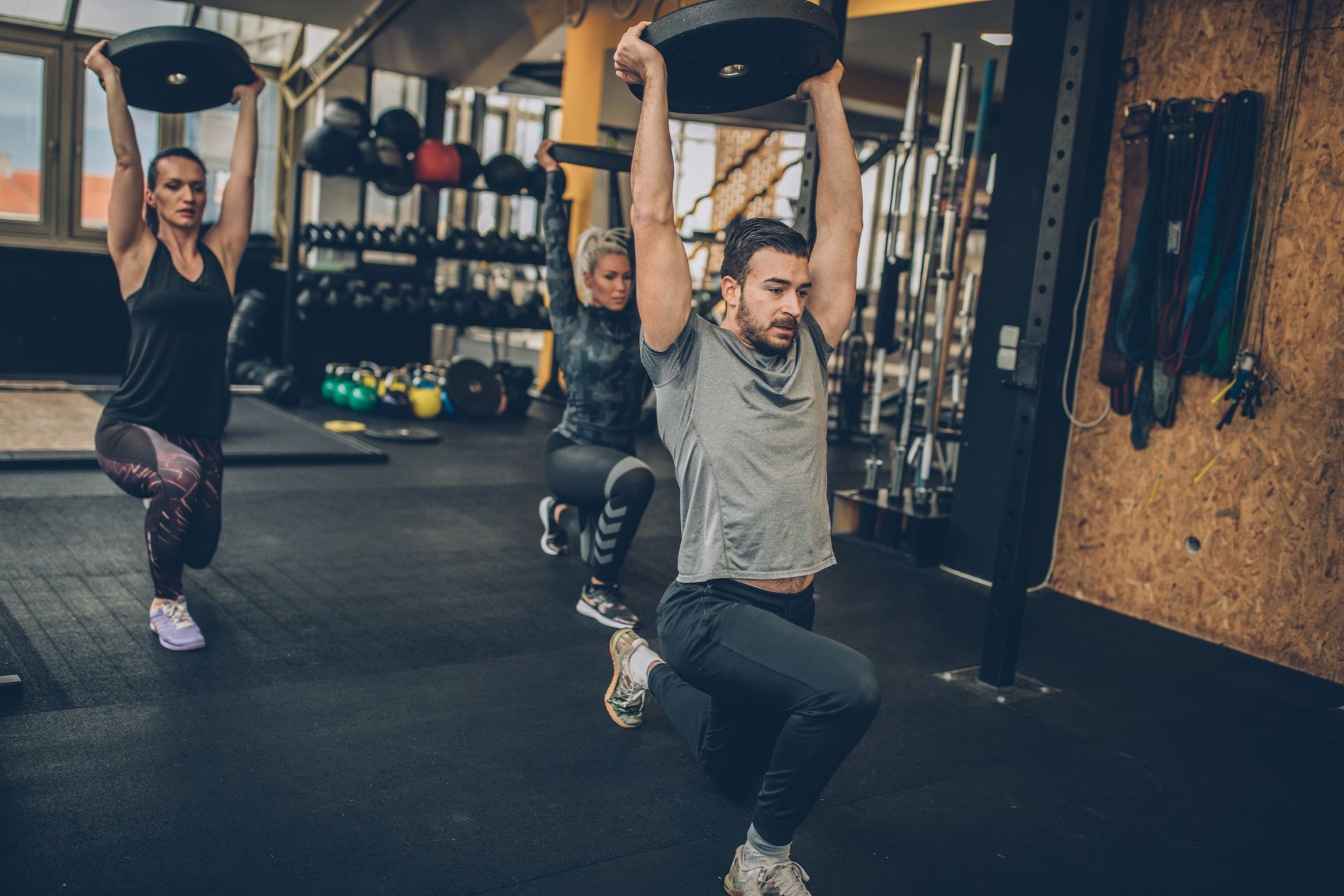

Cupping therapy has been shown to influence tissue perfusion and pain modulation in physical therapy (PT) rehabilitation. The application of negative pressure through the use of cups can lead to increased blood flow, improved microcirculation, and enhanced tissue oxygenation, ultimately promoting tissue perfusion. This can result in accelerated healing, reduced inflammation, and improved tissue repair, which are all crucial components of the rehabilitation process. Additionally, cupping therapy has been found to stimulate the release of endorphins and other neuropeptides, leading to pain modulation and relief. By targeting trigger points and areas of pain, cupping therapy can help alleviate discomfort and improve overall function, making it a valuable adjunct to PT rehabilitation programs.
There are several psychological factors that can influence adherence to home exercise programs. One important factor is motivation, which can be influenced by a person's beliefs, values, and goals. For example, if someone believes that exercise is important for their overall health and has a goal of improving their fitness level, they may be more motivated to stick to their home exercise program. Another factor is self-efficacy, which refers to a person's belief in their ability to successfully complete a task. If someone has high self-efficacy for exercise, they are more likely to believe that they can successfully complete their home exercise program and are therefore more likely to adhere to it. Additionally, social support can play a role in adherence. Having support from friends, family, or a workout buddy can provide encouragement and accountability, making it more likely that a person will stick to their home exercise program. Finally, enjoyment of the exercise itself can also influence adherence. If someone finds their home exercise program enjoyable and engaging, they are more likely to continue with it over time.
Individuals with hypermobility syndromes require exercise programs that are tailored to their specific needs. Therapists modify exercise programs by focusing on stability and strengthening exercises that target the muscles surrounding the hypermobile joints. These exercises aim to improve joint stability and reduce the risk of injury. Therapists also incorporate low-impact exercises, such as swimming or cycling, to reduce the stress on the joints. Additionally, therapists may use props, such as resistance bands or stability balls, to provide additional support during exercises. It is important for therapists to monitor the individual's progress and adjust the exercise program accordingly to ensure that it is effective and safe.
Neurodynamic techniques, such as nerve flossing, tensioning, and sliders, have been shown to be effective in the management of sciatic nerve pain. These techniques involve specific movements and stretches that aim to mobilize and desensitize the sciatic nerve and its surrounding tissues. By addressing neural tension and improving nerve mobility, neurodynamic techniques can help alleviate symptoms associated with sciatic nerve pain, such as radiating leg pain, numbness, and tingling. Additionally, incorporating neurodynamic techniques into a comprehensive treatment plan for sciatic nerve pain may also help improve flexibility, reduce muscle tension, and enhance overall functional mobility. Overall, the use of neurodynamic techniques can be a valuable component in the holistic management of sciatic nerve pain.
The McKenzie Method is commonly used in the treatment of lumbar disc herniation due to its effectiveness in reducing pain and improving function. Indications for using this method include patients experiencing radicular pain, such as sciatica, which is caused by the compression of a nerve root due to the herniated disc. Additionally, patients with symptoms of numbness, tingling, or weakness in the lower extremities may benefit from this treatment approach. The McKenzie Method is also suitable for individuals with a history of recurrent or chronic low back pain, as it aims to address the underlying mechanical dysfunction and promote self-management strategies. Furthermore, patients who prefer a non-invasive and conservative treatment option may find the McKenzie Method appealing, as it focuses on active patient participation through specific exercises and postural modifications.
Compression garments have been found to be effective in reducing edema and improving circulation in individuals who have suffered from injuries. These garments apply pressure to the affected area, which helps to reduce swelling and promote the movement of fluid out of the tissues. By improving circulation, compression garments also aid in the delivery of oxygen and nutrients to the injured area, which can help to speed up the healing process. Additionally, these garments can provide support to the injured area, which can help to reduce pain and discomfort. Overall, the use of compression garments post-injury can be a beneficial adjunct therapy in the management of edema and circulation issues.
Individuals recovering from vestibular disorders can benefit from a variety of balance training exercises that target specific aspects of their condition. One effective exercise is the Romberg test, which involves standing with feet together and eyes closed to challenge proprioception and balance. Another beneficial exercise is the tandem walk, where the individual walks heel-to-toe in a straight line to improve coordination and stability. Additionally, the use of balance boards or stability balls can help improve balance and strengthen the core muscles. Other exercises that can be beneficial include single-leg stands, side-to-side weight shifts, and head movements to stimulate the vestibular system. It is important for individuals recovering from vestibular disorders to work with a healthcare professional to determine the most appropriate exercises for their specific condition and to ensure proper technique and safety.