Frequently Asked Questions
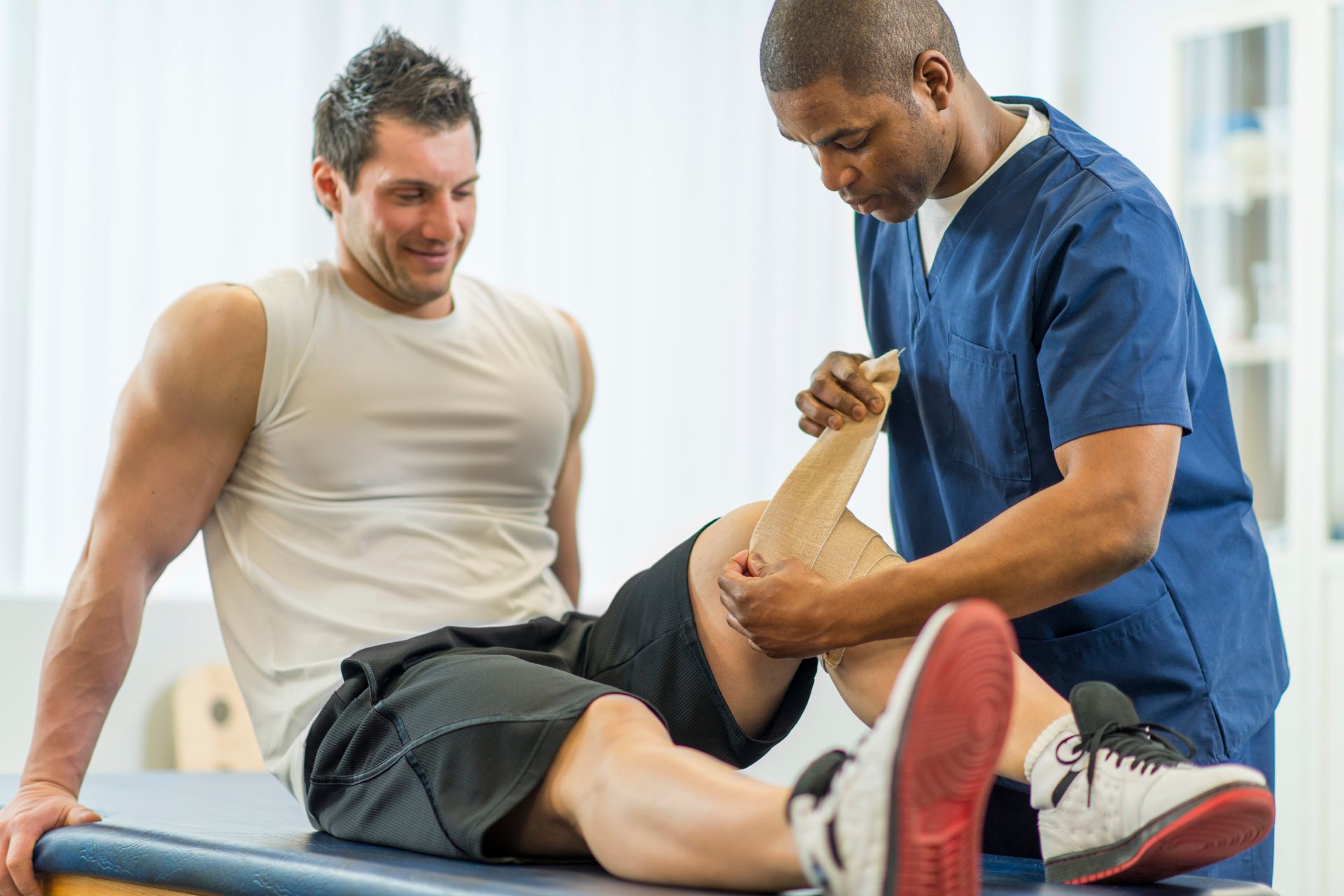
Effective physical therapy techniques for recovering from knee replacement surgery include a structured regimen of range-of-motion exercises, strengthening protocols, and functional training. Initial focus on gentle passive and active-assisted movements helps improve joint flexibility while decreasing stiffness post-operatively. Gradually introducing weight-bearing exercises such as heel slides and leg lifts assists in rebuilding quadriceps strength essential for stability. Closed-chain activities like mini squats or step-ups facilitate proprioception and balance recovery, critical for safe ambulation. Incorporating modalities such as electrical stimulation can enhance muscle activation in the early stages of rehabilitation, while aquatic therapy promotes low-impact resistance to support healing without excessive strain on the surgical site. Regular gait training ensures proper biomechanics during walking patterns, ultimately fostering independence in daily activities as patients transition through various phases of recovery with an emphasis on gradual progression toward higher-level tasks like stair climbing or returning to sports-specific drills when appropriate.
Typically, a patient may begin physical therapy within 24 to 48 hours after spinal fusion surgery, pending the surgeon's approval and the patient's overall stability. The initial session usually focuses on gentle movements and foundational exercises aimed at enhancing mobility while minimizing strain on the surgical site. This early rehabilitation phase incorporates activities such as deep breathing exercises to promote lung expansion, isometric strengthening techniques for core stability without excessive load-bearing, and ambulation practices that facilitate safe walking patterns with appropriate gait training aids if necessary. Additionally, education regarding posture correction and body mechanics plays a crucial role in preventing complications during recovery. Overall, this careful introduction of rehabilitative strategies aims to support healing while progressively increasing functional capacity in alignment with post-operative protocols.
Manual therapy plays a crucial role in post-operative recovery for shoulder surgeries by enhancing mobility, reducing pain, and improving overall function. Techniques such as myofascial release, joint mobilization, and soft tissue manipulation facilitate the reduction of scar tissue formation while promoting lymphatic drainage to decrease swelling. Additionally, these interventions can enhance proprioception and neuromuscular control around the glenohumeral joint following procedures like rotator cuff repair or shoulder stabilization surgery. By addressing restrictions in range of motion through targeted manipulative approaches, manual therapy helps restore optimal biomechanics and supports rehabilitation exercises aimed at strengthening surrounding musculature. Furthermore, it aids in alleviating postoperative discomfort associated with inflammation and muscle guarding that often accompany surgical recovery processes.
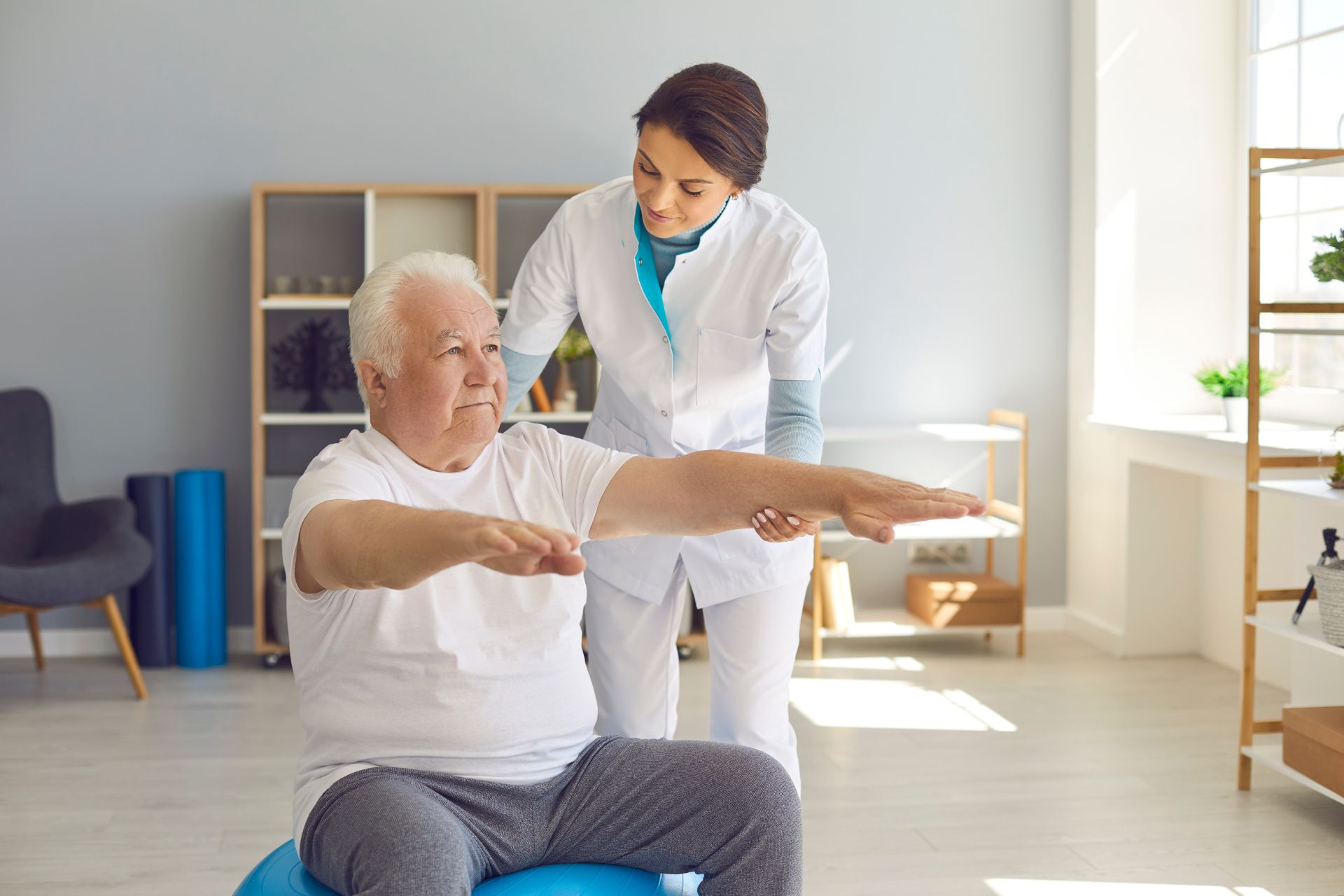
Patients with limited mobility can significantly benefit from personalized home-based physical therapy following hip arthroplasty through tailored rehabilitation programs that focus on enhancing their functional independence and promoting optimal recovery. This individualized approach allows for the integration of specific therapeutic exercises designed to improve strength, flexibility, and balance while addressing unique challenges faced by each patient. Home-based therapy facilitates a comfortable environment where patients can engage in progressive resistance training, gait retraining, and joint mobilization techniques at their own pace. Additionally, therapists can provide education on pain management strategies and adaptive equipment usage to enhance safety during daily activities. By implementing evidence-based interventions within the familiar context of home settings, patients are more likely to adhere to prescribed routines, leading to improved outcomes such as increased range of motion and reduced risk of complications like stiffness or falls post-surgery.
Proprioceptive training plays a crucial role in rehabilitation following ankle ligament reconstruction surgery by enhancing neuromuscular control, balance, and coordination. This type of training focuses on improving the body’s ability to sense its position in space, which is essential for joint stability and functionality. By utilizing exercises that challenge proprioception—such as single-leg stands, wobble boards, and dynamic movements—patients can effectively retrain their musculoskeletal system to respond appropriately during activities of daily living and sports performance. Furthermore, incorporating proprioceptive feedback mechanisms aids in preventing re-injury by reinforcing motor patterns that promote safe movement strategies. Overall, an emphasis on proprioceptive development not only accelerates recovery but also contributes significantly to long-term outcomes such as agility enhancement and reduction of chronic instability associated with previous ankle injuries.